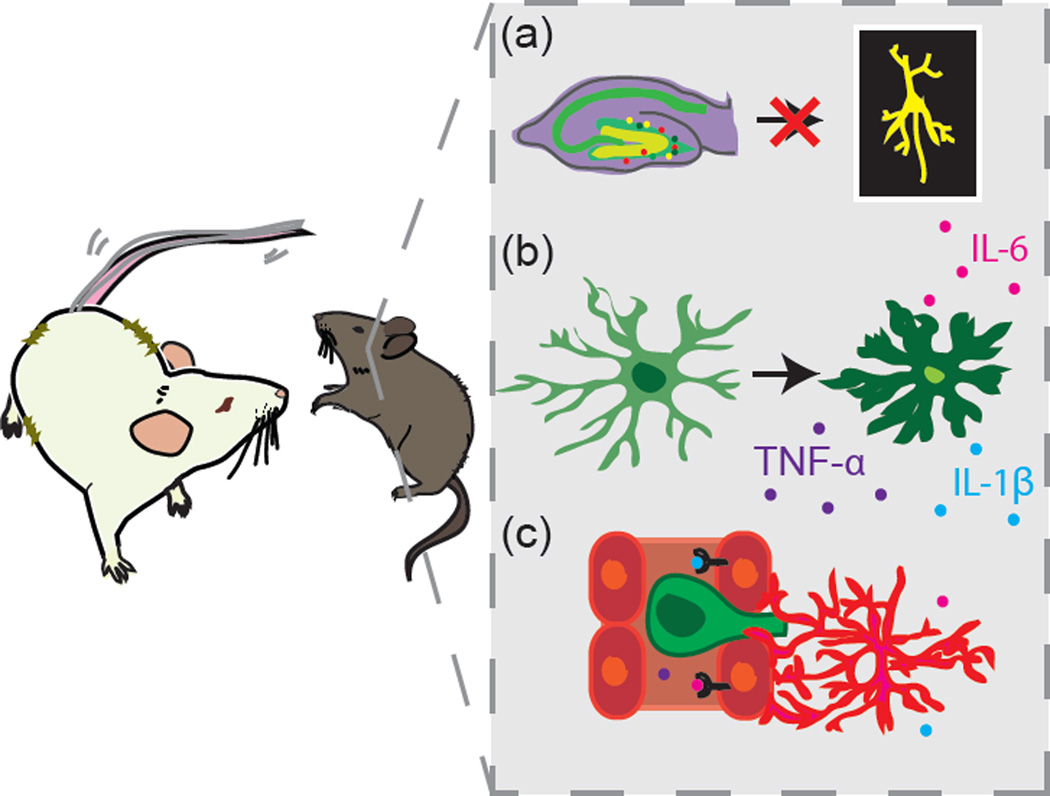
Figure 1. Overview of hippocampal changes following exposure to Repeated Social Defeat (RSD).
A recent publication by McKim et al. [3] finds that RSD produces numerous cellular and molecular consequences in the caudal hippocampus relevant to cognitive function. Changes include reduced differentiation of neural progenitor cells into mature neurons in the dentate gyrus (A), enhanced microglial activation and increased expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (B), and trafficking of monocytes into the brain from the peripheral circulation (C).