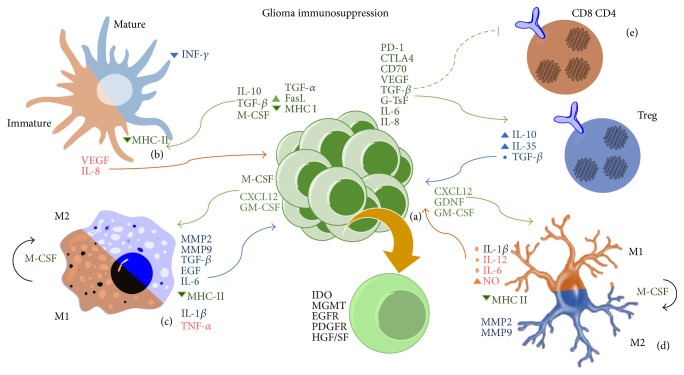
Figure 1.
Diverse mechanisms used by glioma cells to generate immunosuppression. (a) Glioma cells secrete molecules that recruit regulatory T cells and inhibit cytotoxic T cells and Th1 lymphocytes proliferation. They promote the migration of MDSC and acquire an anti-inflammatory phenotype because of molecules like M-CSF. Glioma cells also increase receptors like EGFR and particular enzymes as IDO. (b) There is a predominance of immature DC and mature DC downregulate INF-γ expression. (c) The majority of macrophages population is represented by phenotype M2 which secretes MMP that remodel the extracellular matrix joined to other growth factors. (d) Phenotype M2 macrophages secrete MMP and different growth factors, supplying microglia infiltration. However, M1 profile does not have antitumor effect, because it generates cytokines such as IL-β inducing the expression of TGF-β by tumor cells. (e) Tregs downregulate other lymphocytes populations and are recruited by glioma.