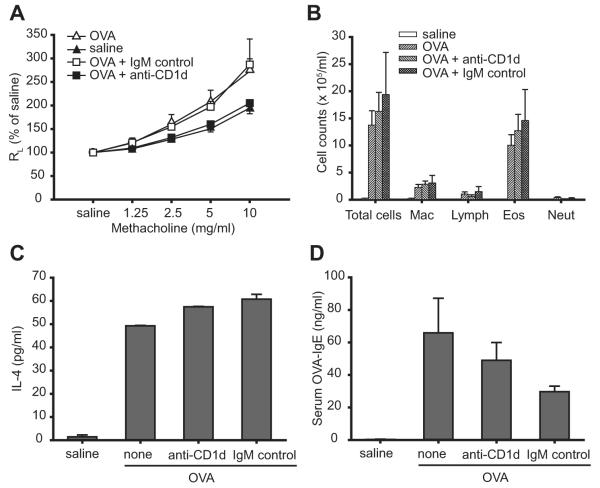
FIGURE 2.
Blockade of CD1d in β2m−/− mice inhibits the development of allergen-induced AHR. A, Treatment with anti-CD1d mAb, but not isotype control mAb, blocks the development of AHR in β2m−/− mice. β2m−/− mice were treated with the 3C11 anti-CD1d or isotype control mAb as described in Materials and Methods and AHR was measured as in Fig. 1A. Data represent the mean ± SEM percentage of saline value from four experiments (n = 4–18). Values of p are 0.001 for OVA + anti-CD1d vs OVA and <0.0001 for OVA + anti-CD1d vs OVA + IgM control. B, Treatment with anti-CD1d mAb does not inhibit the development of eosinophilic airway inflammation in β2m−/− mice. BAL fluid from mice in A, was analyzed as in Fig. 1B. C, Treatment with anti-CD1d mAb does not inhibit OVA-induced IL-4 production from bronchial lymph node T cells in β2m−/− mice. Bronchial lymph nodes from mice in A were removed and analyzed as in Fig. 1C. Lymph node cell cultures were stimulated with 100 μg/ml OVA. D, Treatment with anti-CD1d mAb does not inhibit OVA-specific serum IgE production in β2m−/− mice. OVA-specific IgE from mice in A was measured as in Fig. 1D. See Fig. 1 legend for definitions of abbreviations.