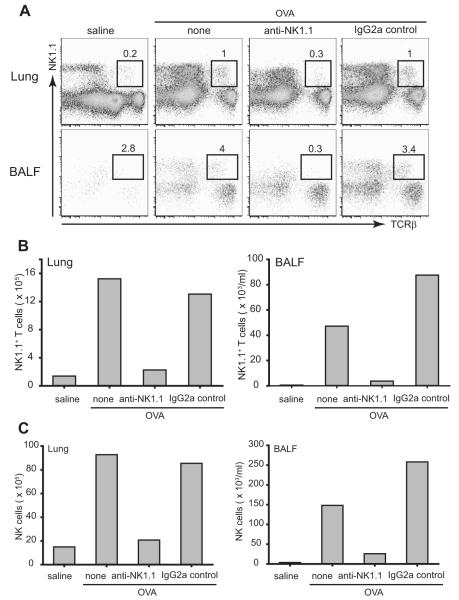
FIGURE 3.
Depletion of NKT cells from lung and airways of β2m−/− mice after treatment with anti-NK1.1 mAb. β2m−/− mice were treated with anti-NK1.1 or isotype control mAb as described in Materials and Methods. A, Lung and BAL fluid (BALF) cells were obtained and pooled 24 h after the last OVA challenge (n = 3) and stained with anti-NK1.1 mAb and anti-TCRβ mAb for evaluation by flow cytometry. Treatment with anti-NK1.1 mAb, but not isotype control mAb, in β2m−/− mice substantially reduced the number of NK1.1+TCRβ+ NKT cells in the lungs and BAL fluid. The number of NKT cells are shown as a percentage of total lymphocytes. B, The absolute number of NKT cells in the lungs and BAL fluid was calculated, and shows that treatment with anti-NK1.1 mAb greatly reduced the number of NKT cells in these compartments. Data are representative of three experiments. C, Depletion of NK cells from lung and airways of β2m−/− mice after treatment with anti-NK1.1 mAb. β2m−/− mice were treated with anti-NK1.1 or isotype control mAb as described in Materials and Methods. Lung and BAL fluid cells were obtained and pooled 24 h after the last OVA challenge (n = 3) and stained with anti-NK1.1 mAb and anti-TCRβ mAb for evaluation by flow cytometry. The proportion of NK1.1+TCRβ− NK cells was obtained and the total cell counts were calculated. Treatment with anti-NK1.1 mAb, but not isotype control mAb, in β2m−/− mice substantially reduced the total counts of NK cells from lung (left) and airways (right), which is representative of three experiments.