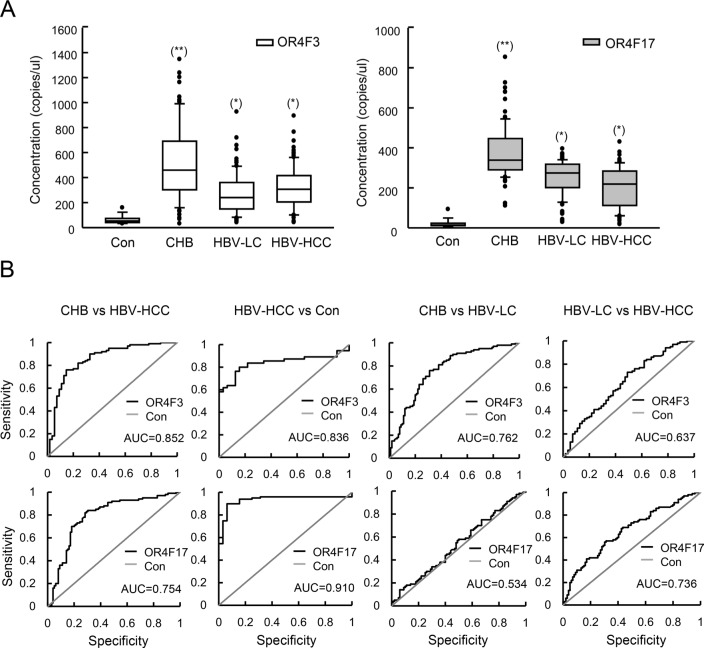
Figure 3. OR4F3 and OR4F17 as biomarkers for HBV-related diseases.
A. Quantification of OR4F3 and OR4F17 levels in healthy controls (n = 20), CHB patients (n = 100), HBV-LC patients (n = 100), and HBV-HCC patients (n = 100). The copy number levels were determined using absolute qPCR. Results are presented as copies per microliter. The unpaired t-test was performed to assess significance of differences between HBV-related groups and control groups. P-values of less than 0.05 were deemed to be significant. (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.005). Control (Con); chronic hepatitis B (CHB); hepatitis B virus-liver cirrhosis (HBV-LC); hepatitis B virus- hepatocellular carcinoma (HBV-HCC); OR4F3, olfactory receptor, family 4, subfamily F, member 3; OR4F17, olfactory receptor, family 4, subfamily F, member 17. B. ROC curves for the OR4F3 and OR4F17 genes between the CHB and HBV-HCC as well as HBV-HCC and normal are presented. OR4F3 yielded AUCs (areas under the ROC curve) of 0.852 for discriminating HBV-HCC from CHB and 0.836 for discriminating HBV-HCC from normal. OR4F17 yielded AUCs of 0.754 for discriminating HBV-HCC from CHB and 0.910 for discriminating HBV-HCC from normal. The ROC curves between CHB and HBV-LC as well as HBV-HCC and HBV-LC are presented. OR4F3 yielded AUCs of 0.762 for discriminating HBV-LC from CHB and 0.637 for discriminating HBV-HCC from HBV-LC. OR4F17 yielded AUCs of 0.534 for discriminating HBV-LC from CHB and 0.736 for discriminating HBV-HCC from HBV-LC. Control (Con).