Figure 5. Overexpression of AQP1 promoted proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells.
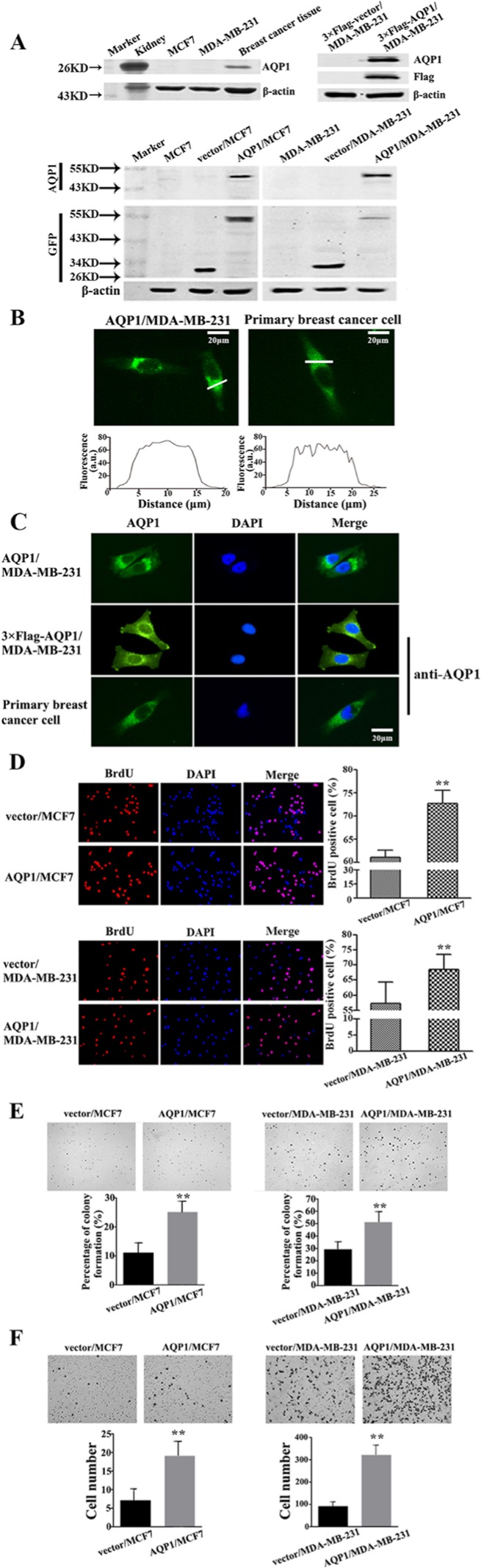
(A) Western blot results of exogenous AQP1 expression in MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 cells. AQP1 expression was detected by primary GFP and AQP1 antibodies in AQP1/MCF7 and AQP1/MDA-MB-231 cells, respectively. AQP1 expression was detected by primary Flag and AQP1 antibodies in 3 × Flag-AQP1/MDA-MB-231 cells. β-actin was used as loading controls. Kidney tissue from mouse was used as a positive control. (B) Cytoplasmic localization of AQP1 was detected in AQP1-overexpressing MDA-MB-231 cells (left panel, AQP1-GFP fusion protein) and primary breast cancer cells (right panel, anti-AQP1 antibody). Fluorescence amplitudes (a.u., arbitrary units) along the line scans (in white on the image) were displayed graphically below each image. (C) Immunofluorescence localization analysis of AQP1 in AQP1-overexpressing MDA-MB-231 cells (upper: GFP labeled AQP1-overexpressing cells; middle: 3 × Flag labeled AQP1-overexpressing cells) and primary breast cancer cells (lower). DAPI was used to stain the nuclei. AQP1 expression was analyzed by GFP fluorescence (upper) and AQP1 antibody (middle and lower). (D) Proliferation ability was detected by BrdU incorporation analysis in AQP1-overexpressing MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 cells (magnification 200 ×). (E) Colony formation assays were performed using AQP1-overexpressing MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 cells (magnification 200 ×). (F) Invasion ability was detected using AQP1-overexpressing MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 cells. Bars are mean ± SD. All experiments were performed 3 times independently. (**P < 0.01)
