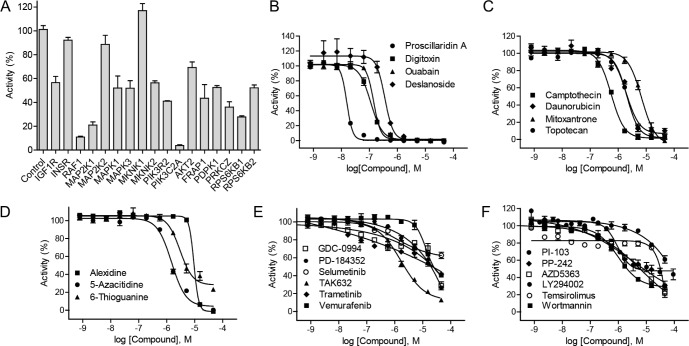
Figure 2. Identification of HIF-1 pathway inhibitors by HIF-1α–NanoLuc assay.
(A) Luciferase signals of HIF-1α–NanoLuc reporter cell line reverse transfected with selected siRNA duplexes under hypoxic (1% O2) conditions. siRNA screening data were expressed as a percentage of the non-targeting control siRNA data, mean ± SD from three measurement. (B) Graph showing a concentration-dependent response of hypoxia-induced HIF-1α-NanoLuc activity to cardiac glycosides: deslanoside, digitoxin, ouabain, and proscillaridin A. (C) Graph showing a concentration-dependent response of hypoxia-induced HIF-1α-NanoLuc activity to of topoisomerase inhibitors: daunorubicin, campthecin, mitoxantrone, and topotecan. (D) Graph showing a concentration-dependent response of hypoxia-induced HIF-1α-NanoLuc activity to nucleoside analogs: alexidine, 5-azacitidine, and thioguanine. (E) Graph showing a concentration-dependent response of hypoxia-induced HIF-1α-NanoLuc activity to RAS–RAF–MEK–ERK pathway inhibitors: GDC-0994, PD-184352, selumetinib, TAK632, trametinib, and vemurafenib. (F) Graph showing a concentration-dependent response of hypoxia-induced HIF-1α-NanoLuc activity to PI3K–AKT–mTOR pathway inhibitors: LY294002, PI-103, PP-242, temsirolimus, and wortmannin. Confirmatory screening data of small molecule inhibitors were expressed as mean ± SD from three measurements.