Figure 1. Identification of aptamer that specifically targets metastatic HCC.
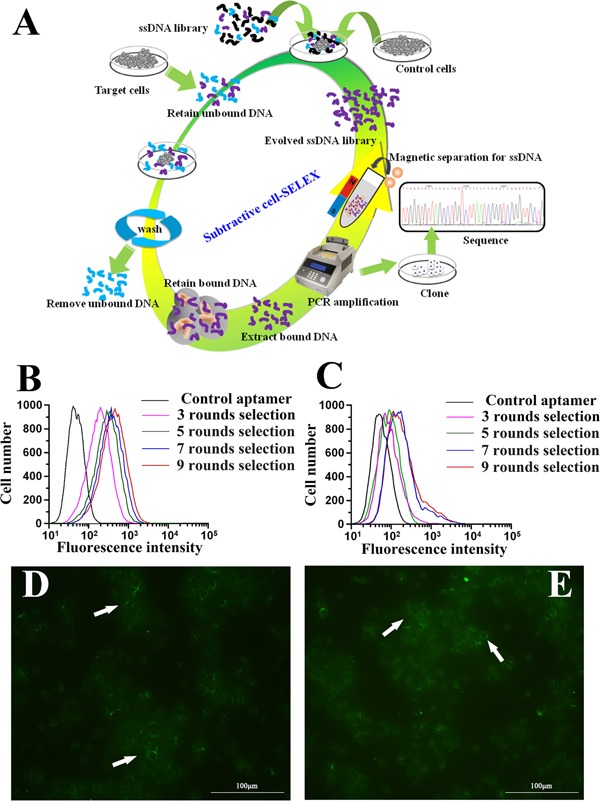
A. Schematics of the cell-based aptamer selection in our study. B, C. Flow cytometry assay to monitor the binding of selected library with HCCLM9 (target cells) and MHCC97L (subtractive cells). B. Increasing fluorescence intensity bound to HCCLM9 with the 3, 5, 7 and 9 rounds of selected library; C. Fluorescence intensity bound on MHCC97L with the 3, 5, 7 and 9 rounds selected library by flow cytomtry. With increasing rounds of enrichment, significant increases in fluorescence intensity were detected on HCCLM9 cells (panel B) but not on MHCC97L (panel C), suggesting the enrichment of HCCLM9 specific aptamers. D. The fluorescence imaging of the 9 rounds selected library bound to HCCLM9 cells by fluorescent microcopy analysis. E. The fluorescence imaging of the 5 rounds selected library bound to HCCLM9 cells by fluorescent microcopy analysis.
