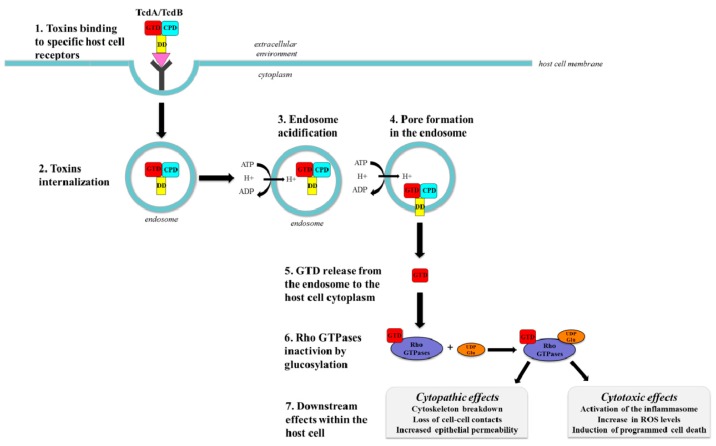
Figure 2.
Toxins delivery into the host cell cytosol can be divided into seven main steps: (1) toxin binding to the host cell surface receptor; (2) toxins internalization through a receptor-mediated endocytosis; (3) endosome acidification; (4) pore formation; (5) GTD release from the endosome to the host cell cytoplasm; (6) Rho GTPases inactivation by glucosylation; and (7) downstream effects within the host cell, i.e., toxins-induced cytopathic and cytotoxic effects. For clarity, the color codes used to depict the diverse toxins domains are the same used in Figure 1: GTD: N-terminal glucosyltransferase domain (red); CPD: cysteine protease domain (cyan); DD: delivery domain (yellow).