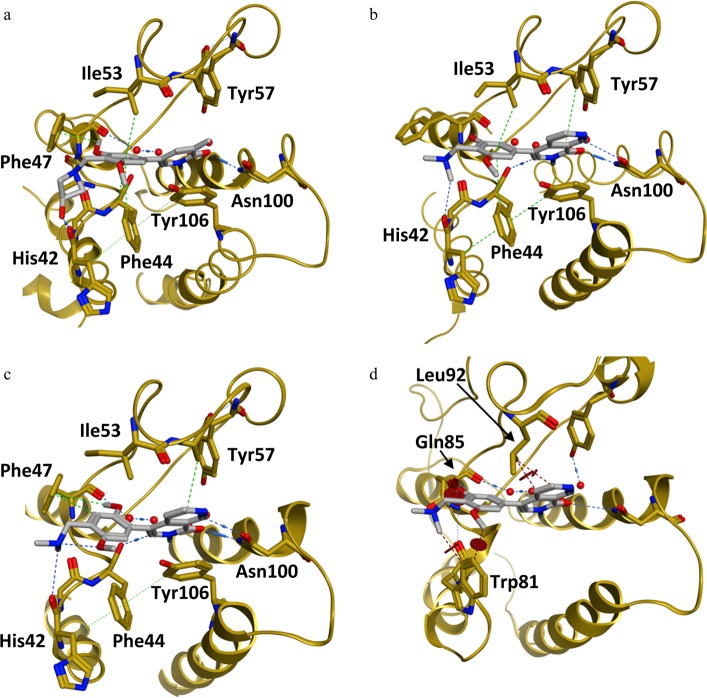
Figure 2.
(a–c) Binding mode of BRD9 BD inhibitors (a) 11, (b) 1, and (c) 2 [compound 11: PDB code 5F1L; compound 1: PDB code 5EU1; compound 2: PDB code 5F1H]. (d) X-ray co-crystal structure of 1 in BRD9 (not shown) aligned with BRD4-BD1 (compound 1: PDB code 5EU1). (a) Binding mode of compound 11 in BRD9 BD: H-bond to Asn100, water-bridged interaction with Tyr57, π-stacking with Tyr106, C–H π-interaction with Ile53, T-stacking with Phe44, H-bond to His42, and induced fit Phe47/C–H π-interaction. (b) Binding mode of compound 1 in BRD9 BD:6 two H-bonds to Asn100, water-mediated hydrogen bond with Tyr57, π-stacking with Tyr106, C–H π-interaction with Ile53, and T-stacking with Phe44. (c) Binding mode of compound 2 in BRD9 BD: two H-bonds to Asn100, water-bridged interaction with Tyr57, π-stacking with Tyr106, C–H π-interaction with Ile53, T-stacking with Phe44,and induced fit Phe47/C–H π-interaction. (d) Clash between 1 and BRD4-BD1 BD amino acids (Trp81, Gln85, and Leu92) is shown (brown circles).