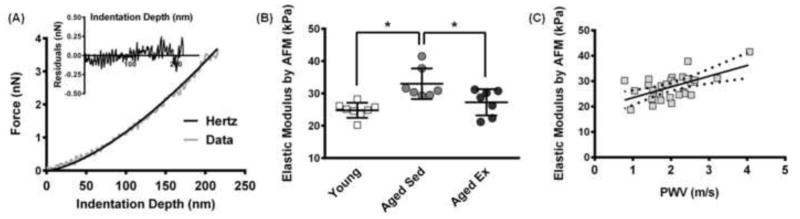
Figure 3.
Micro-scale elastic modulus increases with age and decreases with exercise. (A) Representative Hertz model fit to AFM force-indentation curve, and inset shows the residuals of the Hertz model fit to the data. (B) The mean elastic modulus of the subendothelial matrix in aged-sedentary mice (20 months old, n=7 mice) relative to young mice (4 months old, n=8 mice) and aged-exercised mice (20 months old, n=7 mice) based on AFM measurements, * p<0.01 (Linear Mixed Effects Model, square-root transform). (C) Comparison of PWV macro-scale stiffness with micro-scale AFM elastic modulus values from each mouse, p<0.02 (Linear Mixed Effects Model). The solid line indicates the linear fit and the dotted lines indicate the standard error.