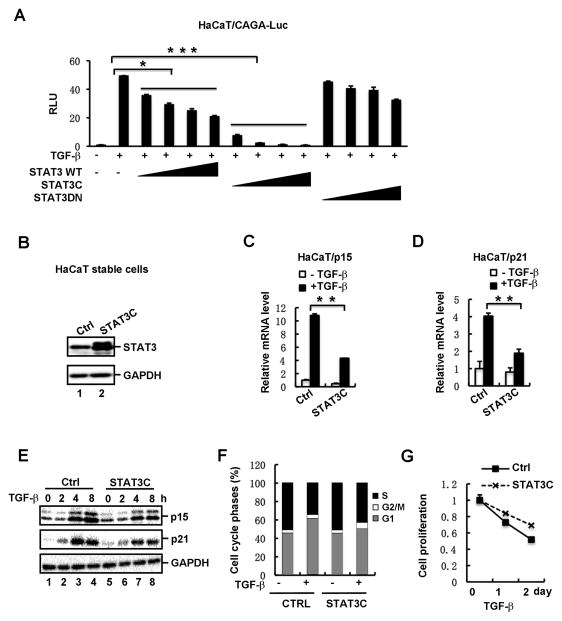
Fig. 2. Activated STAT3 suppresses TGF-β-induced growth inhibitory responses.
(A) STAT3C potently attenuates TGF-β-induced reporter expression in a dose-dependent manner. HaCaT cells were transfected with increasing amounts of STAT3 wildtype (WT) or variants (STAT3C or STAT3DN), together with CAGA-Luc, and then treated with or without TGF-β (2 ng/ml).
(B) Stable expression of STAT3C in HaCaT cells. The protein level of STAT3 was detected by using Western blotting. Note that the protein level of exogenous Flag-STAT3C is similar to that of endogenous STAT3.
(C) Stable expression of STAT3C decreases TGF-β-induced p15 mRNA expression in HaCaT cells. Cells were treated with or without TGF-β (2 ng/ml) for 2h, and total RNA was extracted for qRT-PCR analysis.
(D) STAT3C decreases TGF-β-induced p21 mRNA expression in HaCaT cells.
(E) Stable expression of STAT3C decreases TGF-β-induced p15 and p21 protein expression in HaCaT cells. Cells were treated with TGF-β for 0, 2, 4 and 8 h, respectively, and then the protein levels of p15 and p21 were detected by using Western blotting.
(F) STAT3C promotes G1-S progression in TGF-β-treated cells. STAT3C cells and control cells were treated with TGF-β (2 ng/ml) for 2 days. Cell cycle progression was determined by flow cytometry as described under “Materials and Methods”.
(G) STAT3C interferes with TGF-β-mediated inhibition on cell proliferation. STAT3C stable cells and control cells were treated with TGF-β, and cell growth rates were examined by actual cell numbers being counted at indicated time point (0, 1 and 2 d) of TGF-β treatment.