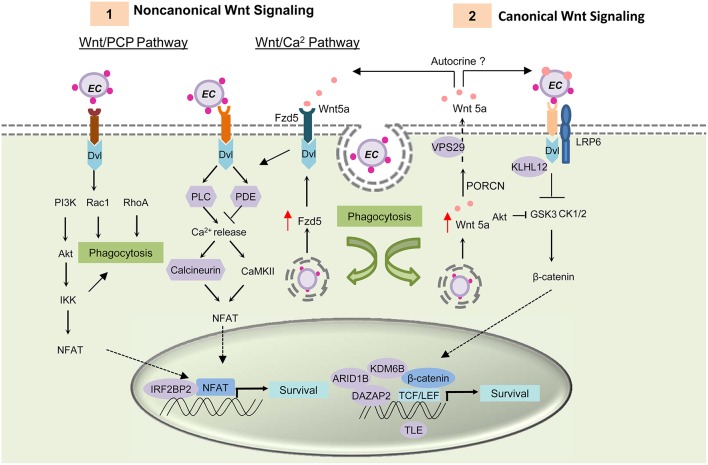
Figure 3.
E. chaffeensis mediated activation of Wnt signaling pathway and function. TRP proteins interacts with unknown Wnt receptors and activating both canonical and noncanonical Wnt signaling through activation of Dvl. (1) Activation of the Wnt/PCP pathway and the Wnt/ Ca2+ pathway causes translocation of transcription factor NFAT to the nucleus and results in target gene expression. TRP induced activation of noncanonical Wnt pathway activation triggers phagocytosis and helps in bacterial internalization. After internalization, E. chaffeensis induces expression of the receptor Fzd5 and possibly the ligand Wnt5a. Interaction of Wnt5a with Wnt receptor Fzd5 causes increased Ca2+ release and NFAT translocation to nucleus. This signaling plays a major role in ehrlichial survival. (2) Both ehrlichial TRPs and Wnt5a can interact with the unknown receptor and LRP6 co-receptor and activate canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Activation of canonical Wnt signaling results in dephosphorylation and translocation of β-catenin into the nucleus within 1 h p.i. Unphosphorylated β-catenin associates with TCF/LEF family of transcription factors and causes induction of Wnt target genes. Activation of these genes are essential for ehrlichial survival. TRPs interact with important components and regulators of Wnt pathway (shown in purple) and thus regulate Wnt signaling.