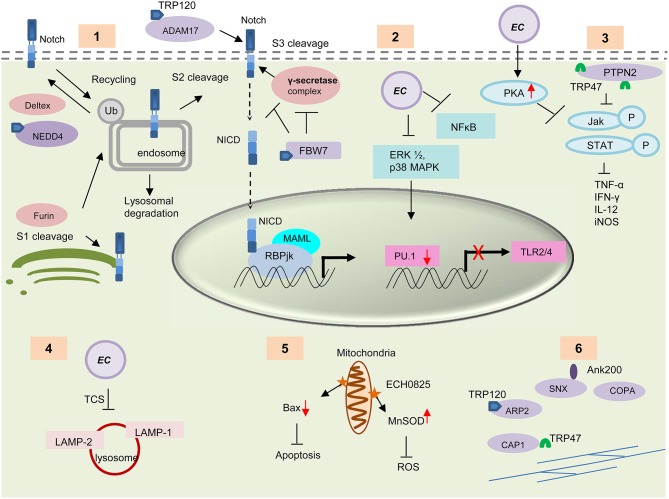
Figure 4.
Survival strategies used by E. chaffeensis during intracellular development. (1) TRP120 interacts with some important enzymes involved in the activation and regulation of host Notch signaling pathways e.g., ADAM17, NEDD4L, and FBW7. These TRP-protein interactions might play an important role in modulation and exploitation of the Notch pathway. (2) E. chaffeensis causes decreased PRR (TLR 2 and 4) expression through downregulation of ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK cell signaling molecules and subsequent inhibition of PU.1 transcription factor. (3) Interaction of TRP47 with host protein PTPN2 or induction of host cell protein kinase A (PKA) by Ehrlichia causes inhibition of IFN-γ mediated tyrosine phosphorylation of JAk/STAT and thus causes decreased cytokine production. (4) E. chaffeensis uses a two component system (TCS) for the inhibition of phagosome lysosome fusion and thus protect itself from degradation by autophagy. (5) The effector protein ECH0825 protects Ehrlichia from ROS by induction of MnSOD and inhibits Bax mediated apoptosis. (6) TRPs interact with host cytoskeletal proteins to facilitate exocytosis or filopodium formation, which helps direct cell to cell transfer. TRP interacting proteins are shown in purple.