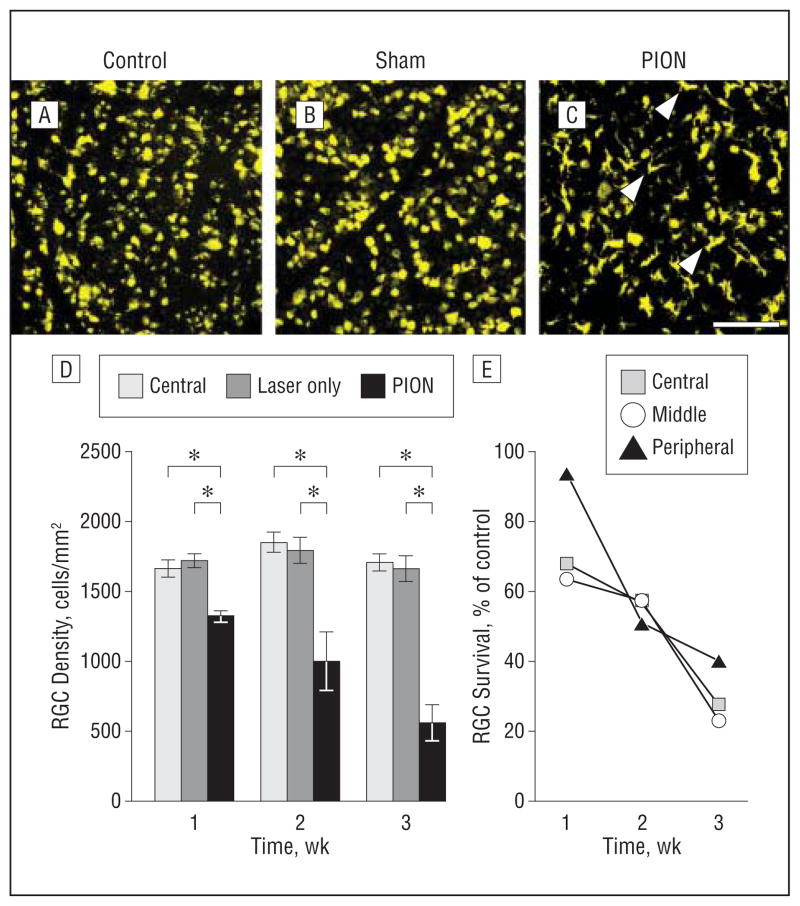
Figure 8.
Temporal characterization of retinal ganglion cell (RGC) survival after posterior ischemic optic neuropathy (PION). Retinal ganglion cells retrograde labeled with fluorogold and representative images of flat mounted retinal segments approximately 2 mm from the optic disk are shown (A–C). In the normal control (A) and sham-treated (B, laser only/no erythrosin B) eyes, RGCs are labeled with punctate fluorescence. C, Two weeks after PION induction, the number of fluorogold-labeled RGCs is markedly reduced. Some of the ameboid, densely fluorescent cells are microglia, which phagocytose fluorogold from dead RGCs (arrowheads). D, RGC quantification demonstrated no difference in the number of fluorogold-labeled RGCs between normal control animals and sham-treated animals at different points after surgery. However, the number of fluorogold-labeled RGCs is decreased in a time-dependent manner after PION induction. These decreases are statistically significant (error bars indicate mean [standard error of the mean]; *P<.001; 1-way analysis of variance; n=4 animals per group). E, RGC survival rate at different points after injury in the central, middle, and peripheral areas of the retina. Scale bar=100 μm.