Fig. 2.
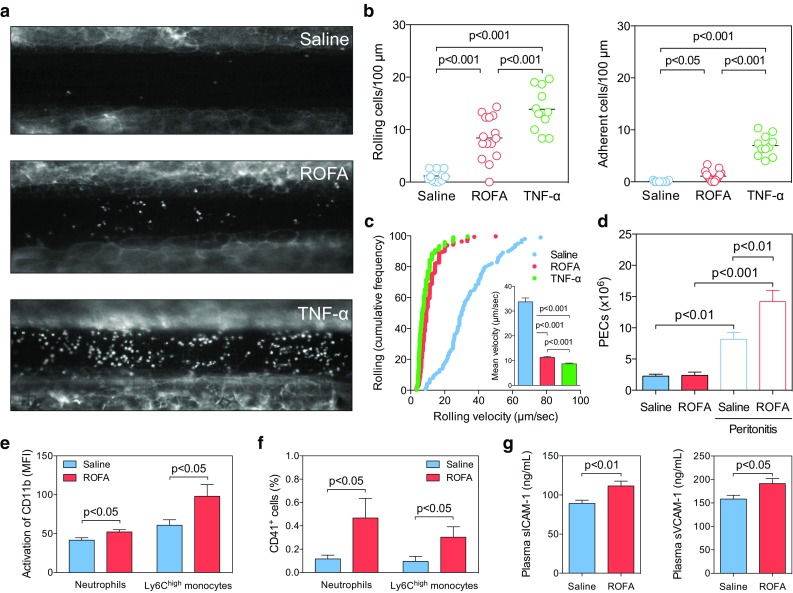
A single instillation of ROFA particles promotes adhesion and migration of pro-inflammatory leukocytes. C57BL/6J mice were treated with either saline, a suspension of ROFA particles in saline (1 mg/kg body weight), or murine TNF-α (200 ng i.p.) as positive control. After 3 h, leukocyte recruitment in mesenteric venules was assessed in intravital microscopy. Leukocytes were stained by rhodamine (a) and leukocyte rolling, adhesion (b), and cumulative frequency of the rolling velocity (c) were quantified. The inlay in c represents leukocyte mean rolling velocity. To evaluate whether ROFA treatment primes leukocytes to migrate, the number of cells residing in the peritoneal cavity (PECs) was quantified in saline- or ROFA-exposed mice. Leukocyte migration was forced by inducing sterile peritonitis by an i.p. injection of 4 % thioglycollate broth (d). To assess leukocyte activation, expression of the CD11b activation epitope (CRBM1/5, e) and formation of leukocyte-platelet aggregates (f) were quantified on myeloid cells by flow cytometry. Plasma markers of endothelial activation (g) were quantified by ELISA. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of at least 10 mice per group
