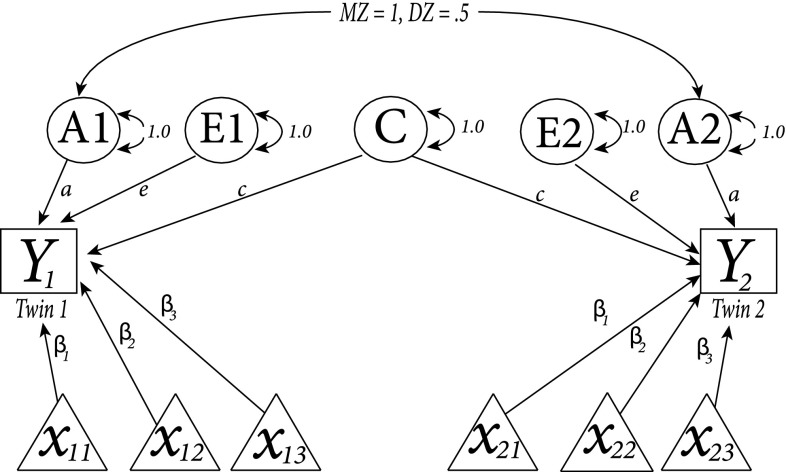
Fig. 1.
Structural equation model (SEM) for a basic univariate twin analysis (ACE model) extended with three covariates (denoted as and for the first and as , and for the second twin of a family). Y denotes the phenotypic values of the first (Y1) and second (Y2) twin and A refers to additive genetic influences for the first (A1) and second (A2) twin, which are correlated 0.5 in dizygotic twins and 1 in monozygotic twins. E1 and E2 denote unique-environmental influences of the first and second twin respectively and are assumed to be uncorrelated. C, common-environmental influences, are the same for all family members. Double-headed arrows denote (co-)variances. The path coefficients, , , , a, c and e represent regression coefficients that express the estimated effect of the respective influences