Figure 1.
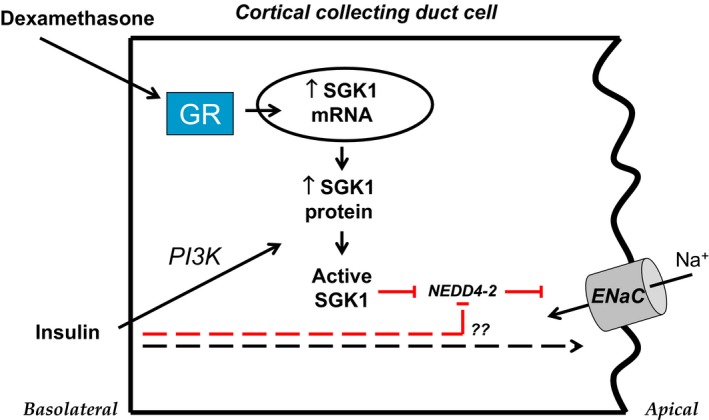
Model of insulin action in the cortical collecting duct. In cultured cortical collecting duct cells, dexamethasone activates glucocorticoid receptors (GR) which rapidly stimulate transcription of SGK1 mRNA and translation of SGK1 protein. Insulin or IGF‐1 (not pictured) activates PI3K which induces phosphorylation and activation of SGK1 protein. Once activated, SGK1 phosphorylates and inhibits the E3 ubiquitin ligase Nedd4‐2. Under basal conditions, Nedd4‐2 decreases expression of ENaC in the apical cell membrane by promoting channel ubiquitination and retrieval. Upon inhibition of Nedd4‐2 by SGK1, ENaC residency in the apical membrane increases, leading to apical entry of Na+ into the cell. A parallel pathway may enable insulin to stimulate ENaC in the absence of PI3K or SGK1 activity (dashed lines). Stimulatory pathways are delineated in black; inhibitory pathways are in red.
