Figure 2.
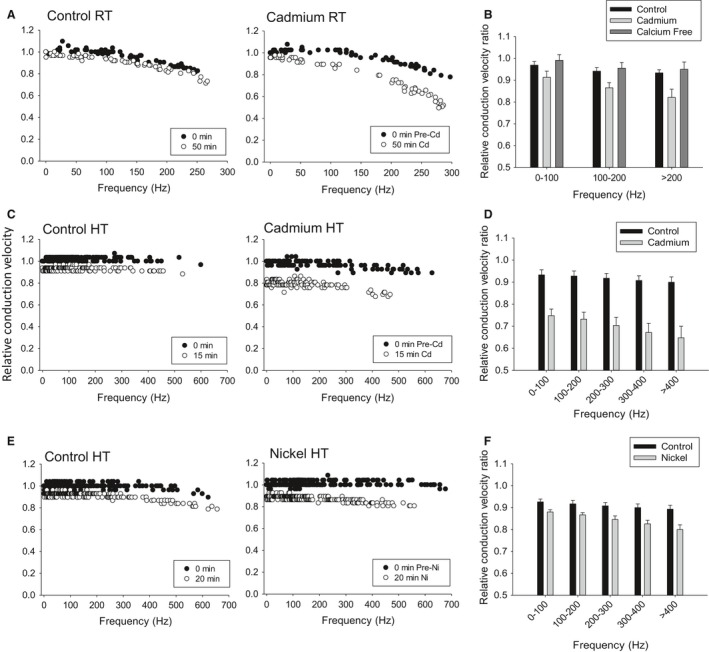
Divalent cations reduce conduction in the DCMD axon. (A) Relative CV profiles show decreased CV after 50 min of exposure to 10 mmol/L of cadmium at room temperature (RT). (B) Relative conduction velocity ratios show cadmium had a significant main effect, reducing velocity while removing extracellular calcium (Calcium Free) caused no changes (Controls: n = 9; Cadmium: n = 8; Calcium free: n = 5; Two‐way ANOVA with Holm–Sidak pairwise multiple comparisons, df = 2, F = 13.2, P < 0.001). (C) Relative CV profiles after 15 min exposure to cadmium at 35°C (HT). (D) Relative CV ratios show cadmium at 35°C had a significant main effect after 15 min (Control: n = 6; Cadmium: n = 7; Two‐Way ANOVA, df = 1, F = 108.0, P < 0.001). (E) Relative CV profiles after 20 min exposure to nickel at 35°C. (F) Relative CV ratios show nickel at 35°C had a significant main effect after 20 min (Control: n = 7; Nickel: n = 6; Two‐Way ANOVA, df = 1, F = 41.7, P < 0.001).
