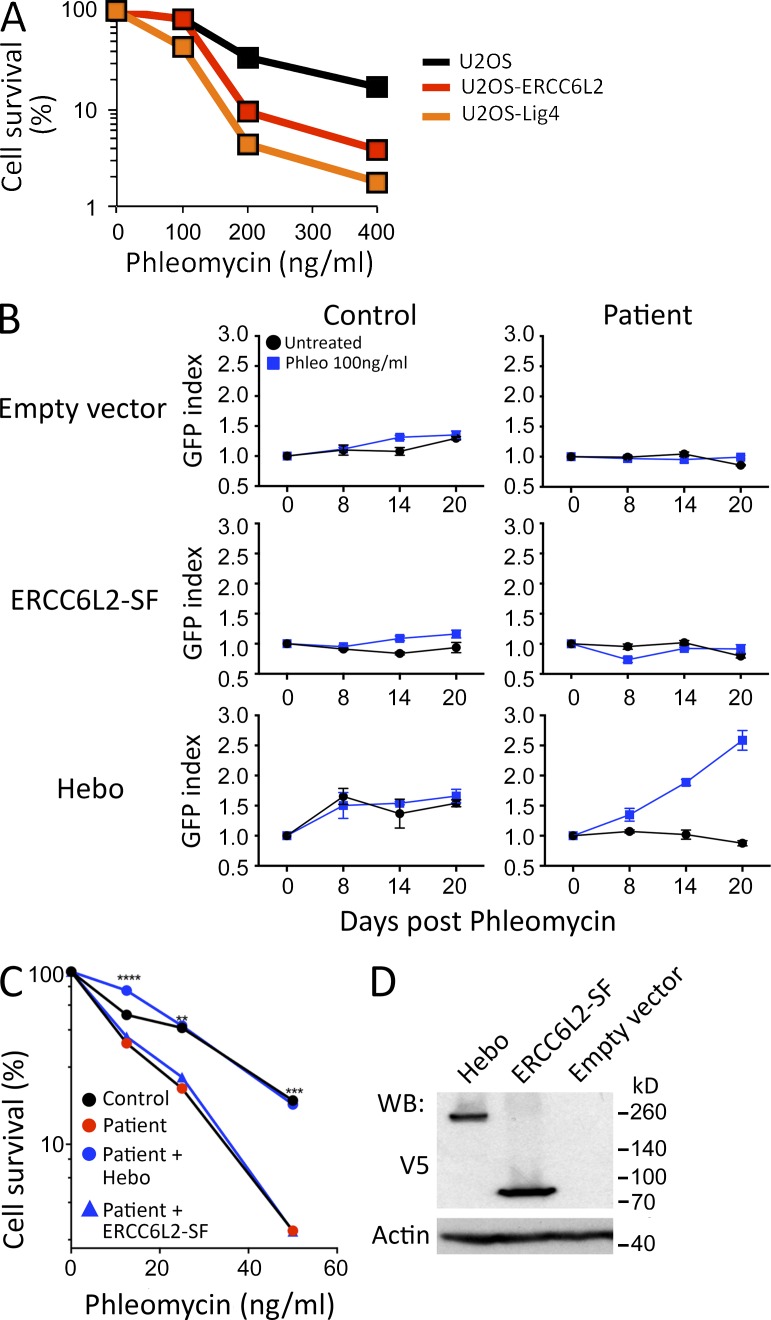
Figure 5.
Functional complementation. (A) Phleo sensitivity of U20S cells, in which the ERCC6L2 gene has been disrupted through CRISPR/Cas9 technology, compared with the sensitivity of the WT parental cells and a U2OS line with mutated DNA ligase IV. This experiment was performed three times. (B) Functional complementation of phleo sensitivity provided by WT Hebo transduced into the patient’s cells as compared with the ERCC6L2-SF or empty vector. A mix population of transduced (GFP+) and untransduced (GFP−) was analyzed through multicolor competition assay (Smogorzewska et al., 2007). The selective growth advantage is scored as the increase in the index of GFP-positive cells/GFP-negative cells at various times compared with the initiation of the culture (index = 1). This experiment was performed two times. Data are mean ± SEM. (C) Sensitivity of the patient’s cells to phleo after Hebo, ERCC6L2-SF, or mock transduction. **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001 for a Mann-Whitney test. This experiment was performed three times. (D) Expression level of Hebo and ERCC6L2-SF after transient transfection into 293T cells, revealed with anti-V5 antibody. WB, Western blot.