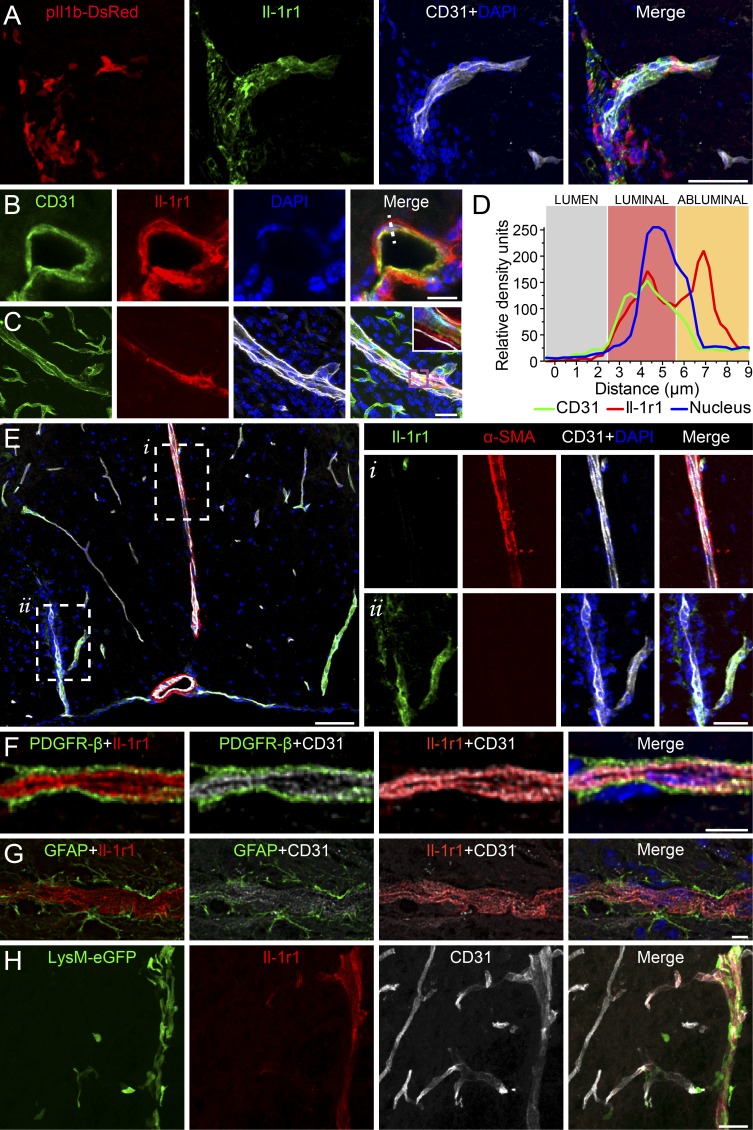
Figure 6.
IL-1R1 is expressed by ECs of the pial venous plexus, which corresponds to the primary site of myeloid cell infiltration during acute EAE. (A–G) Immunofluorescence confocal microscopy of spinal cord tissue sections from EAE C57BL/6 mice. (A) Immunofluorescence was used to assess whether DsRed+ cells are found in proximity of CD31+ ECs and IL-1R1+ blood vessels at onset of EAE. (B and C) IL-1R1 expression on ECs in a naive (B) and inflamed (C) spinal cord. The inset in C is a closeup image of the purple box. (D) Graph displaying the abluminal localization of IL-1R1 on ECs (white dashed line in B). (E) Confocal microscopy was used to assess colocalization (or lack thereof) of IL-1R1+ blood vessels with αSMA, a protein associated with smooth muscle cells in the tunica media of the artery wall (see insets). (F and G) Triple immunofluorescence staining was performed to assess colocalization of IL-1R1 with CD31, PDGFR-β (pericytes), or GFAP (astrocytes). (H) Myeloid cells (LysM-GFP+) were seen to infiltrate almost exclusively through IL-1R1+ blood vessels. Bars: (A) 10 µm; (B and H) 25 µm; (E insets) 50 µm; (E) 100 µm; (F and G) 5 µm.