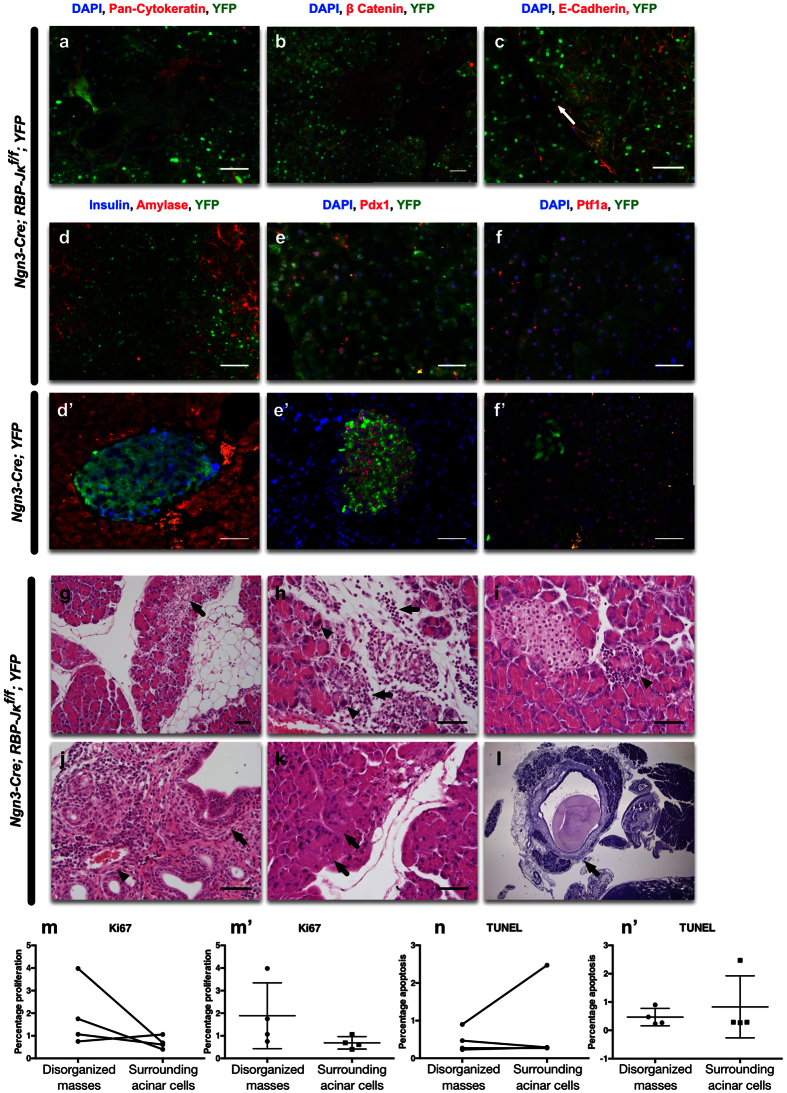
Figure 5. Histological assessment of the disorganized structures in the RBP-Jκ mice.
Immunostaining on RBP-Jκ mice with YFP (green), and either (a) pan-Cytokeratin (red), (b) β-Catenin (red), (c) E-Cadherin (red). (d) Insulin (blue) and Amylase (red); (e) Pdx1 (red); or (f) Ptf1a (red). All nuclei were counterstained in blue with DAPI. (g–l) Hematoxylin and eosin staining on the adult Ngn3-Cre; RBP-Jκf/f Z/EG mice that present disorganized masses. H&E staining showed: (g) focal or spotty injury/necrosis of acinar cell and acinar to ductal metaplasia (arrow) in acinar parenchyma, accompanied by focal fibrosis and inflammatory infiltrates in the stroma; (h) acinar cell injury/necrosis (arrow heads) and inflammatory infiltrates (arrows) shown at high magnification; (i) focal acinar injury/necrosis surrounded by inflammatory response (arrow). (j) Periductal (main and interlobular) (arrow) and perivascular (arrow head) inflammatory infiltrates, composed mainly of lymphocytes and a number of eosinophils; (k) degenerative acinar cells displayed multinucleated syncytia and abundant cytoplasm (arrows); (l) stromal fibrosis and dilated interlobular ducts containing protein plug (arrow) indicating chronic pancreatitis. (m) Assessment of the percentage of proliferating Ki67+ cells in the disorganized masses and in the adjacent acinar cells (represented unpaired in m’). (n) Assessment of the percentage of apoptotic TUNEL+ cells in the disorganized masses and in the adjacent acinar cells (represented unpaired in n’). Scale = 50 μm.