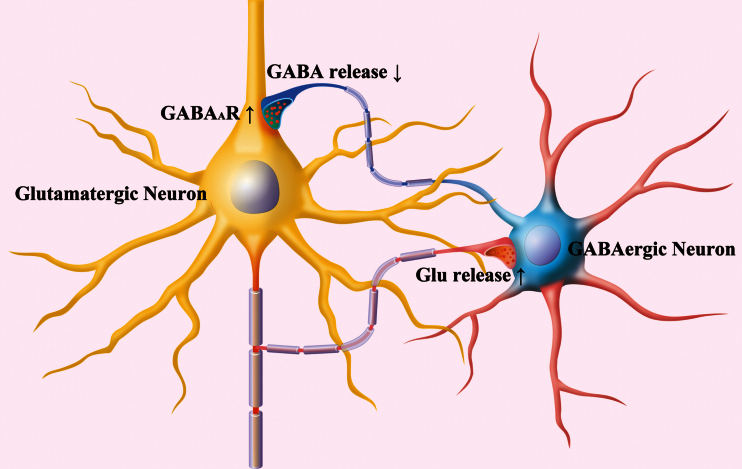
Figure 9.
Incompatible alternations occur in the GABAergic neurons and glutamatergic neurons of the prelimbic cortices from depression-like mice. In GABAergic neurons (round), their intrinsic property and synaptic outputs decrease (blue). Their receptions from excitatory synaptic transmission and innervations as well as their receptive fields increase (red). The incompatibility among the subcellular compartments of GABAergic neurons reduces their efficiency to coordinate their downstream neurons. In glutamatergic neurons (pyramidal), their responses to GABAergic inputs increase, their spiking capability does not change, and their excitatory outputs increase. These incompatible changes among the subcellular compartments of glutamatergic neurons attenuate their efficiency to program the neural codes. Together, these changes, the interactions between GABAergic and glutamatergic neurons, are deteriorated.