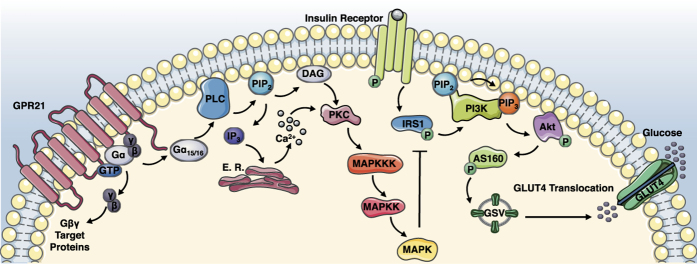
Figure 4. Proposed role for GPR21 in the development of type 2 diabetes.
The constitutively active GPR21 recruits and activates Gα15/16, which facilitates the hydrolysis of PIP2 into DAG and IP3 through the action of PLC. Both DAG and IP3 activate PKC, which signals to and activates the MAPK cascade. The MAPK JNK plays a crucial role in the development of insulin resistance as it promotes the phosphorylation of a key component of the insulin signalling cascade, IRS1, at Ser307, thereby preventing insulin-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of this protein. GPR21-induced activation of the MAPKs may contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes. Due to the potential of a native inverse agonist in serum, GPR21 signal transduction is believed to be tightly regulated under normal physiological conditions. However in a state of obesity, elevated GPR21 activity may become deleterious, potentially promoting the genesis of insulin resistance.