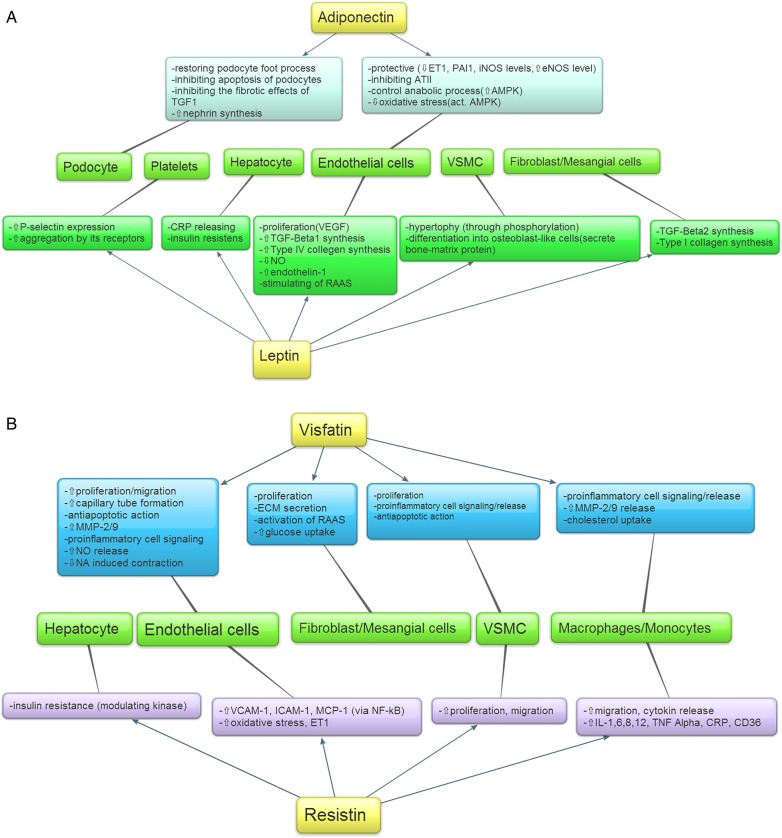
Fig. 1.
(A) Effects of leptin and adiponectin on different types of cells. (B) Effects of visfatin and resistin on different types of cells. ATII, angiotensin II; CRP, C-reactive protein; ECM, extracellular matrix; eNOS, extracellular nitric oxide synthetase; ET1, endothelin-1; ICAM, intracellular adhesion molecule; IL, interleukin; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthetase; MCP, methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; Na, sodium; NF-kB, nuclear factor κB; NO, nitric oxide; PAI1, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1; RAAS, renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system; RAAS, renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system; TGF, transforming growth factor; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; VCAM, vascular cell adhesion molecule; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; VSMC, vascular smooth muscle cell.