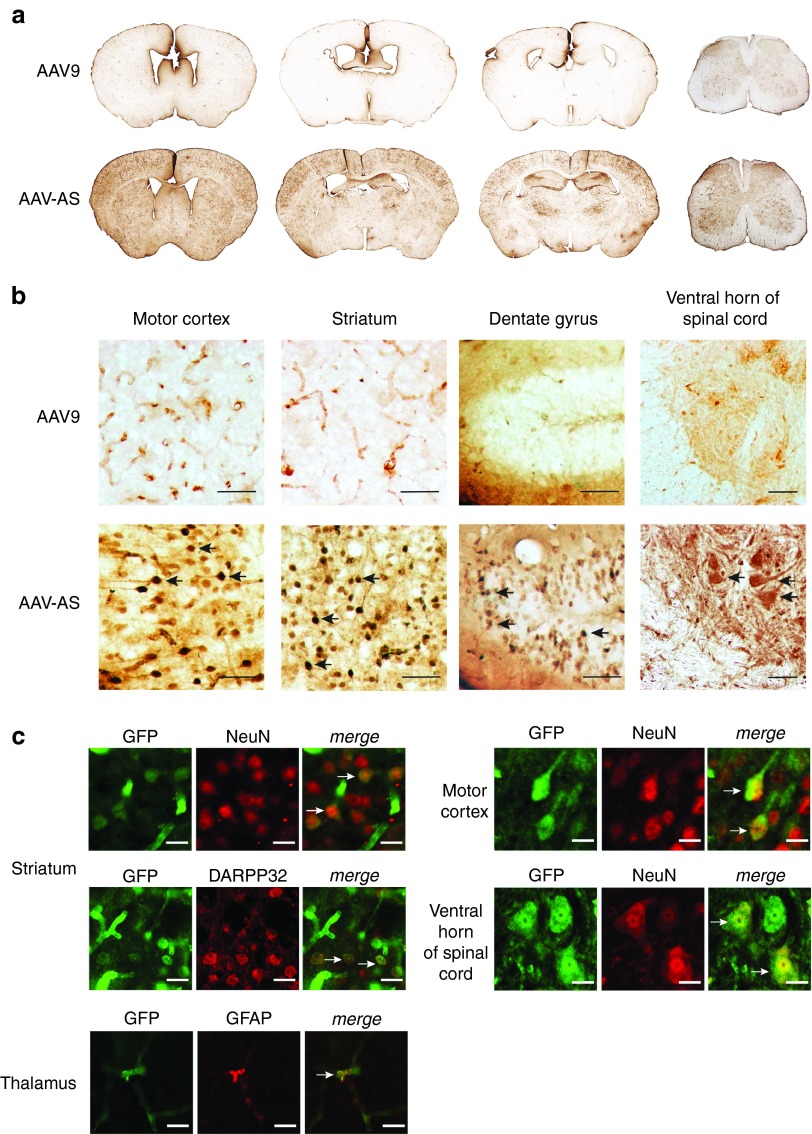
Figure 2.
Central nervous system transduction profile of AAV-AS vector after vascular infusion in adult mice. (a) Overview of GFP distribution in brain and spinal cord in AAV-AS and AAV9 injected mice (5 × 1011 vg/mouse). Representative images of coronal brain sections located in relation to bregma at +0.5, −0.5, and −1.80 mm, and cervical spinal cord (left to right) are shown. (b) Transduction of neuronal populations in different brain regions. Black arrows indicate examples of GFP-positive neurons identified by morphology. Bar = 50 µm. (c) Phenotype of transduced cells was identified by double immunofluorescence staining with antibodies to GFP, pan-neuronal marker NeuN, striatal medium spiny neuron marker DARPP32 or astrocyte marker glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP). Neuronal transduction in spinal cord was examined in sections stained for GFP and NeuN. The large size and morphology of GFP-positive neurons in the ventral spinal cord suggest a motor neuron identity. White arrows indicate examples of GFP-positive neurons. Bar = 10 µm.