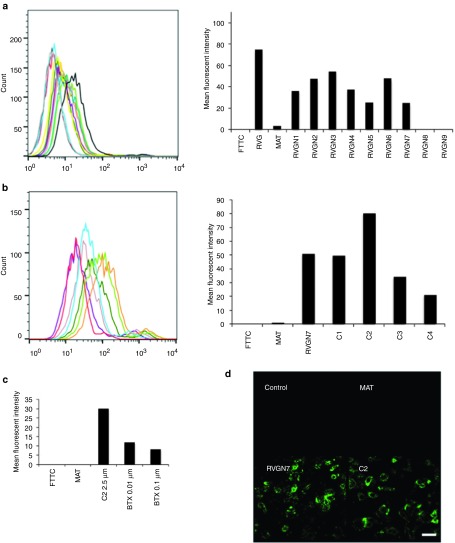
Figure 1.
Identifying the shortest fragment of RVG29 peptide for neuronal binding in vitro. (a) M17 cells were incubated with biotinylated RVG-29 (dark grey), MAT (black), RVGN1 (yellow), RVGN2 (teal), RVGN3 (purple), RVGN4 (mauve), RVGN5 (dark green), RVGN6 (light green), RVGN7 (orange), RVGN8 (turquoise), RVGN9 (red) or FITC (light grey), and stained with avidin-FITC before analysis by flow cytometry. Representative histogram with the mean fluorescence intensity of the peptides bound to M17 cells is shown. (b) M17 cells were incubated with biotinylated RVGN7 (orange), MAT (turquoise), C1 (light green), C2 (dark green), C3 (mauve), C4 (purple), or FITC (red), and stained with avidin-FITC before analysis by flow cytometry. Representative histogram with the mean fluorescence intensity of the peptides bound to M17 cells is shown. (c) M17 cells were incubated with biotinylated-C2 peptide in the absence or presence of competitive antagonist alpha bangarotoxin (BTX) peptide, stained with avidin-FITC and analyzed by flow cytometry. Histogram representing the mean fluorescence intensity of C2 peptide bound to M17 cells as determined by FACS is shown. (d) M17 cells were incubated with or without biotinylated peptides, stained with avidin-FITC and viewed by confocal microscopy. Bar = 200 μm.