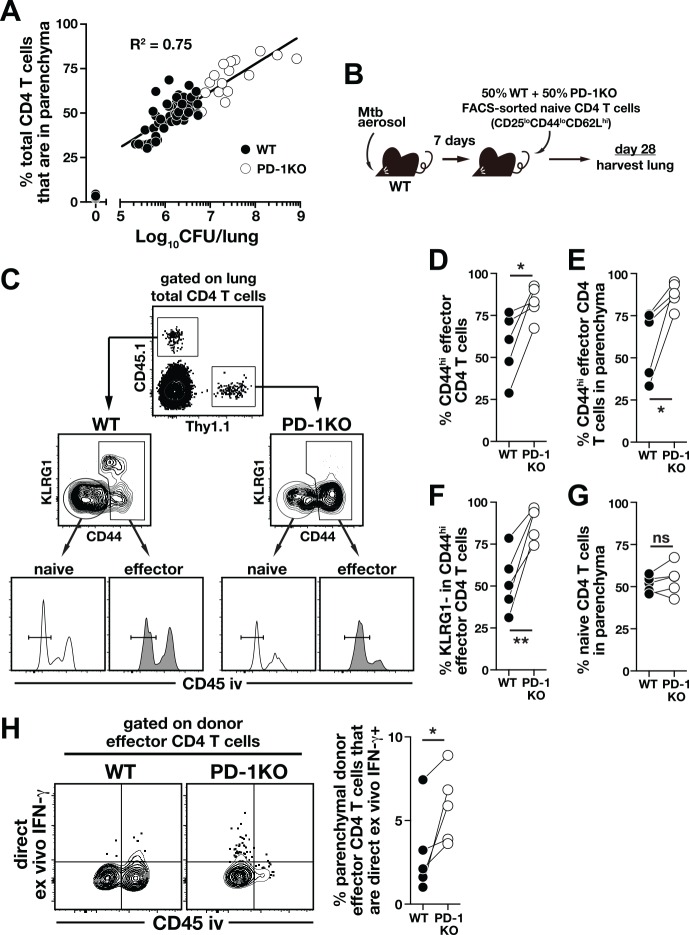
Fig 5. PD-1 expression on CD4 T cells inhibits accumulation of and IFN-γ production by lung parenchymal CD4 T cells during Mtb infection.
(A) Correlation between bacterial load and frequency of parenchymal CD4 T cells in the lungs of Mtb infected mice. Data are pooled from experiments performed at different times p.i. ranging from day 0 to day 180. (B-F) FACS purified naïve CD4 T cells from WT (CD45.1) and PD-1 KO (Thy1.1) mice were mixed at a 1:1 ratio and co-transferred into day-7 infected WT mice (B). On day 28 an iv-stain was performed in the recipient mice and donor CD4 T cells were identified by their congenic markers (C). The frequency of donor total CD44hi effector CD4 T cells in the recipient lungs (D) and in the lung parenchyma (E). (F) The frequency of KLRG1- cells in the donor CD44hi effector CD4 T cells. (G) The frequency of donor naïve CD4 T cells accumulating in the lung parenchyma. (H) IFN-γ production of donor effector CD4 T cells was determined by DrxICS. Data are representative of two independent experiments (n = 5/experiment) and each connecting line represents an individual mouse (n = 5/experiment). *, P<0.02; **, P<0.006.