Figure 6. Suppression of ATR-101 cytotoxicity by structurally dissimilar lipophilic antioxidants.
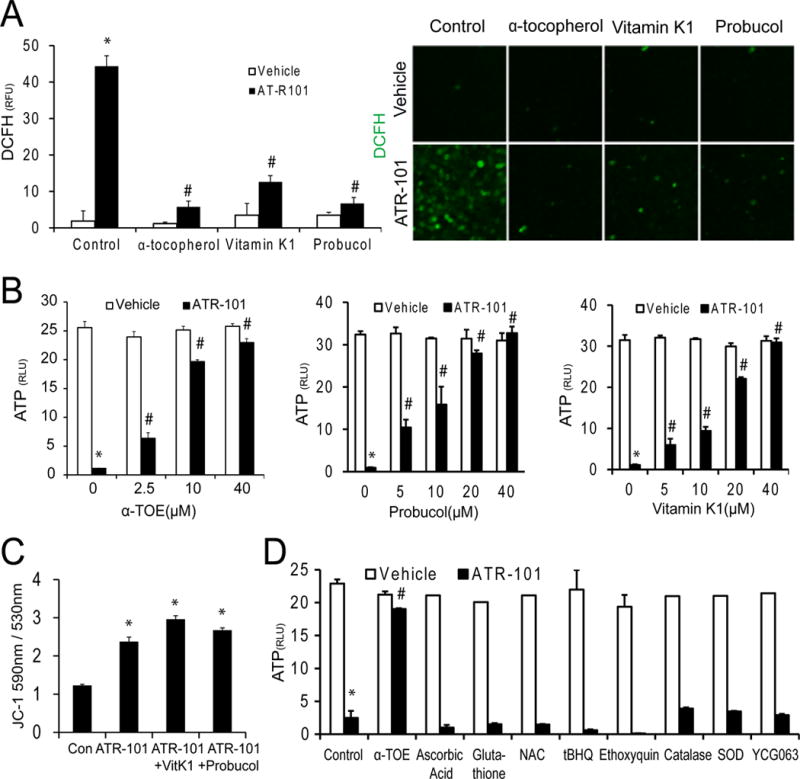
(A) Effects of structurally dissimilar antioxidants on the levels of reactive oxygen species in cells cultured with ATR-101. The images and the graph show the DCFH fluorescence of H295R cells that were cultured with vehicle or with 40 μM ATR-101 together with or without 40 μM α-tocopherol, 3-phytylmenadione (Vitamin K), or probucol for 6 hours, followed by incubation with DCFH (green).
(B) Effects of α-tocopherol, probucol and Vitamin K on the changes in ATP levels caused by ATR-101. The graphs show the ATP levels of H295R cells that were cultured with the indicated concentrations of α-tocopherol (left graph), probucol (middle graph) or Vitamin K (right graph) in combination with 25 μM ATR-101 or vehicle for 20 hours.
(C) Effects of 3-phytylmenadione (Vitamin K) and probucol on the mitochondrial membrane potentials of cells cultured with ATR-101. The graph shows the JC-1 fluorescence emissions ratio (590 nm/530 nm) of H295R cells that were cultured with vehicle or 40 μM ATR-101 alone or in combination with 40 μM 3-phytylmenadione or probucol or for 3 hours.
(D) Effects of various hydrophilic antioxidants on the ATP levels of cells cultured with ATR-101. The graph shows the ATP levels of H295R cells that were cultured with 25 μM ATR-101 or vehicle in combination with 40 μM α-tocopherol, 1 mM Ascorbic Acid, 10 mM Glutathione, 5 mM NAC, 10 μM tBHQ, 20 μM Ethoxyquin, 500 U/ml Catalase, 500 U/ml SOD, or 5 μM YCG063 for 20 hours.
Each graph plots the means and standard deviations of three replicate cultures and is representative of data from two independent experiments (*: p<0.05 vs vehicle, #: p<0.05 vs ATR-101; two-tailed unpaired Student’s t tests). The images are representative of the large majority of cells in each population and of two or more independent experiments.
