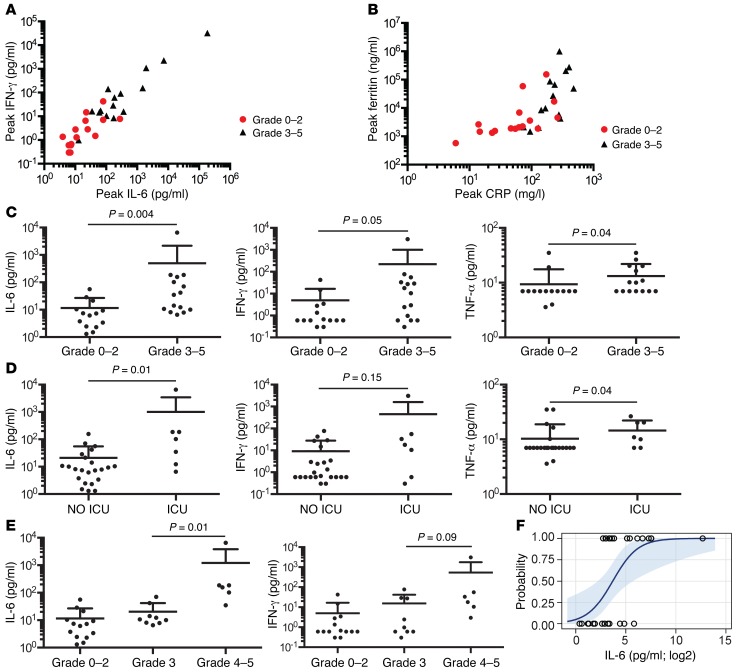
Figure 3. Relationship between serum cytokine, ferritin, and CRP levels and severe neurotoxicity.
(A) The peak IL-6 and IFN-γ concentrations in serum in the first 28 days after CAR–T cell infusion in patients who developed NCI CTCAE grade 3 or higher neurotoxicity (n = 15) compared with those without neurotoxicity (n = 15). (B) The peak ferritin and CRP concentrations in serum in the first 28 days after CAR–T cell infusion in patients who developed NCI CTCAE grade 3 or higher neurotoxicity (n = 15) compared with those without neurotoxicity (n = 15). (C) Serum IL-6, IFN-γ, and TNF-α concentrations on day 1 after CAR–T cell infusion in patients who subsequently developed grade 3 to 5 neurotoxicity compared with those without neurotoxicity. Data represent the mean ± SEM. The Mann-Whitney U test was used for statistical analysis. (D) Serum IL-6, IFN-γ, and TNF-α concentrations on day 1 after CAR–T cell infusion in patients who subsequently required ICU care compared with those who did not require ICU care. Data represent the mean ± SEM. The Mann-Whitney U test was used for statistical analysis. (E) Serum IL-6 and IFN-γ concentrations on day 1 after CAR–T cell infusion in patients who subsequently developed the indicated grades of neurotoxicity. Data represent the mean ± SEM. (F) Predicted probability curve with bounding 95% CI limits showing the relationship between log2-transformed serum IL-6 concentration on day 1 after CAR–T cell infusion and the occurrence of grade 3 or higher neurotoxicity. Circles, observed; line, predicted.