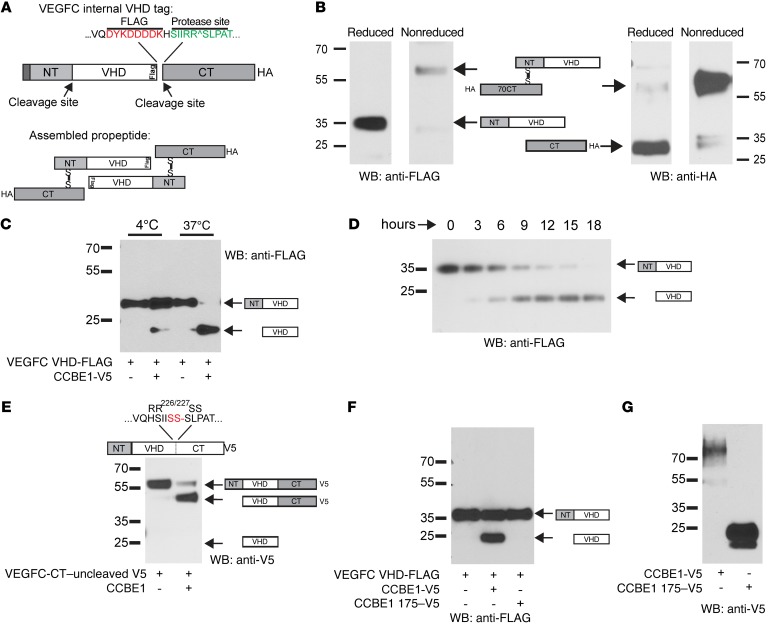
Figure 2. VEGFC VHD-FLAG demonstrates increased VEGFC proteolysis with full-length but not truncated CCBE1.
(A) Schematic of the VEGFC VHD-FLAG protein, in which a FLAG epitope (shown in red) is inserted in frame at the C-terminal end of the VHD. The CT cleavage site is shown in green; an HA tag is placed in frame at the end of the protein CT. Disulfide bonds are predicted to link 2 full-length VEGFC VHD-FLAG molecules as shown in the bottom panel. (B) Detection of VEGFC VHD-FLAG with a C-terminal HA tag under reduced and nonreduced conditions using anti-FLAG and anti-HA Abs. The protein domains within the detected bands are illustrated schematically. (C and D) CCBE1-FL drives VEGFC proteolysis in vitro. HEK293T conditioned media containing VEGFC VHD-FLAG alone or VEGFC VHD-FLAG plus CCBE1-V5 were incubated for 24 hours at 4°C or 37°C prior to detection of FLAG by immunoblotting (C). Temporal analysis revealed slow proteolysis of VEGFC in the presence of CCBE1 (D). (E) N-terminal cleavage of VEGFC was independent of C-terminal cleavage. A VEGFC VHD-FLAG protein containing a mutation that prevents C-terminal cleavage (RR226-227SS) was incubated with CCBE1-V5 or control conditioned medium for 24 hours. (F and G) A truncated form of CCBE1 lacking its C-terminal collagen-like domain failed to drive VEGFC cleavage. VEGF VHD-FLAG was incubated with control conditioned medium, conditioned medium containing full-length CCBE1-V5, and conditioned medium containing CCBE1 175-V5 for 24 hours prior to anti-FLAG immunoblot analysis (F). Full-length CCBE1-V5 was detected as a 70- to 100-kDa smear that was expressed at lower levels than the 25-kDa CCBE1 175-V5 (G). Data shown are representative of 3 separate experiments. WB, Western blot.