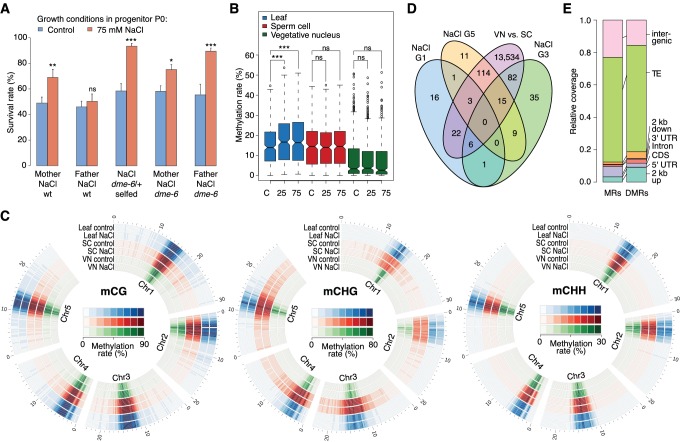
Figure 4. Parent-of-origin effects on stress-induced epimutations.
(A) Survival of F1 seedlings derived from reciprocal crosses between Col-0 wild type or dme-6 mutants that had been exposed to hyperosmotic stress for two generations and untreated wild-type (wt), or progeny of dme-6/+ selfed plants (unpaired Student’s t-test; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ns p>0.05). (B) Absolute methylation frequency differences in DMRs in different tissues from control and stress-treated plants (unpaired, two-sided Student’s t-test; ***p<0.001, ns p>0.05). C, control; 25, 25 mM NaCl; 75, 75 mM NaCl. (C) Genome-wide methylation levels in leaves and pollen derived from control and salt-stressed P0 plants (generation G1). Methylation frequency was calculated as the average methylation frequency of cytosines in a 250 kb window. Chr, chromosome. (D) Overlap of DMRs from the comparison of vegetative nuclei and sperm cells with DMRs identified in leaf tissue after salt treatment in G1, G3, G5. (E) Annotation of MRs and DMRs in vegetative nuclei and sperm cells.