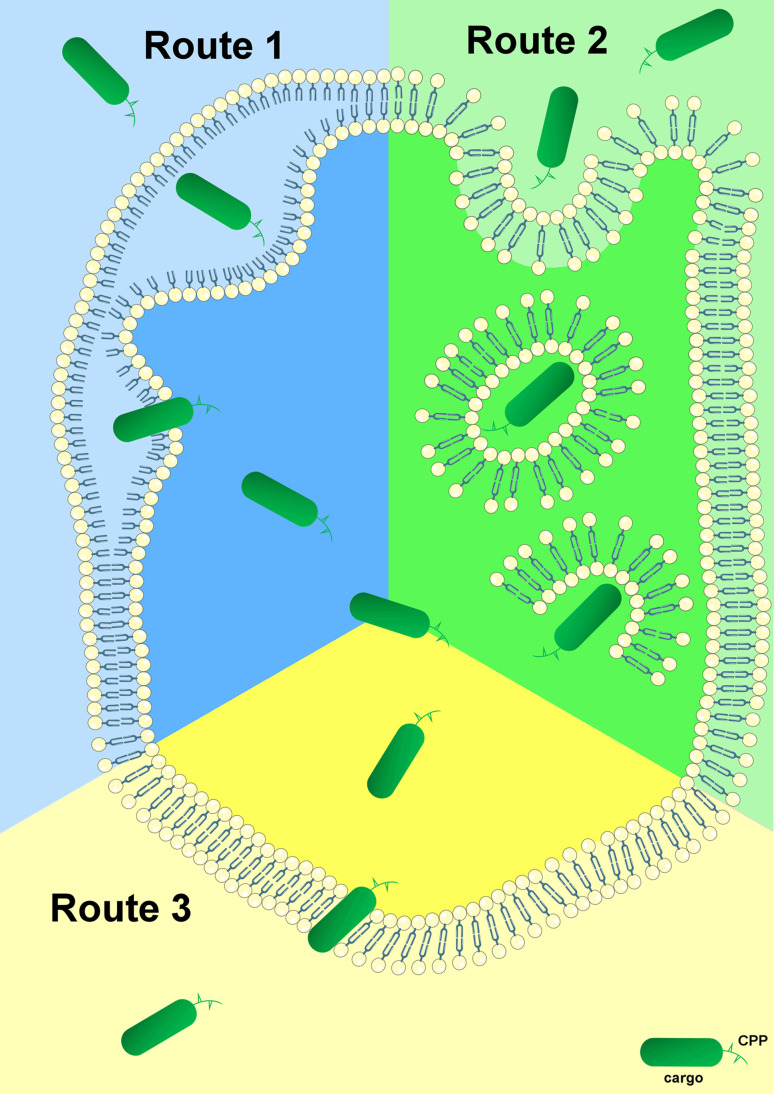
Fig. 1.
Proposed mechanisms for cellular internalization of CPPs. First of all, each CPP-conjugate binds to the plasma membrane via electrostatic interactions. Subsequently, the complete conjugate is internalized and released through various conceivable mechanisms. Route 1 represents cell entry of the CPP-complex through the formation of an inverted micelle (aggregates of colloidal surfactants in which the polar groups are concentrated in the interior and the lipophilic groups extend outward into the solvent). The majority of CPPs probably enter cells by an endocytosis-driven pathway which is depicted as Route 2. Route 3 is a direct, energy- and receptor-independent penetration and transduction process of the construct through the plasma membrane