Figure 8.
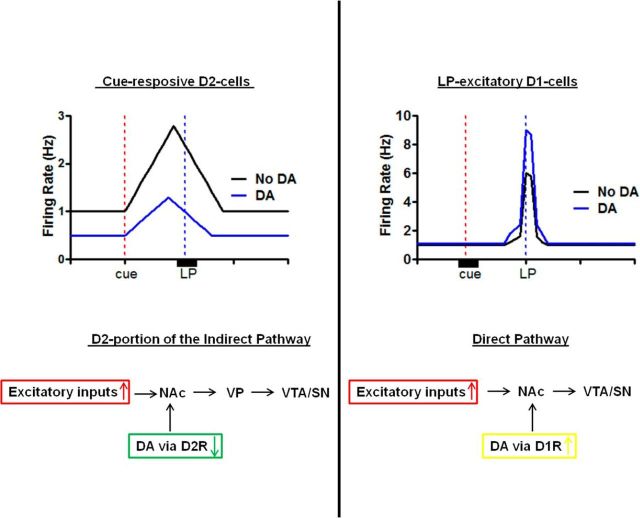
Overview of temporal sequence of MSN cell-firing patterns and neural pathways activated during the ICSS task. Shown is a schematic diagram of the major cell-firing patterns and relationship to MSNs containing specific dopamine receptors during the ICSS behavioral sequence. After the cue, excitatory input activates D2-containing MSNs. Dopamine release in response to the cue suppresses this activation via D2Rs. The net result is that the inhibitory projection to the ventral pallidum (VP) described by Kupchik et al. (2015) is suppressed. Shortly before the rat presses the lever for the electrical stimulation, a separate population of MSNs that contains D1Rs is excited. Dopamine release triggered by the cue is still present and promotes this excitation. The net result of this is that the inhibitory actions of the MSNs that project to the VTA (Kupchik et al., 2015) are enhanced.