Figure 2.
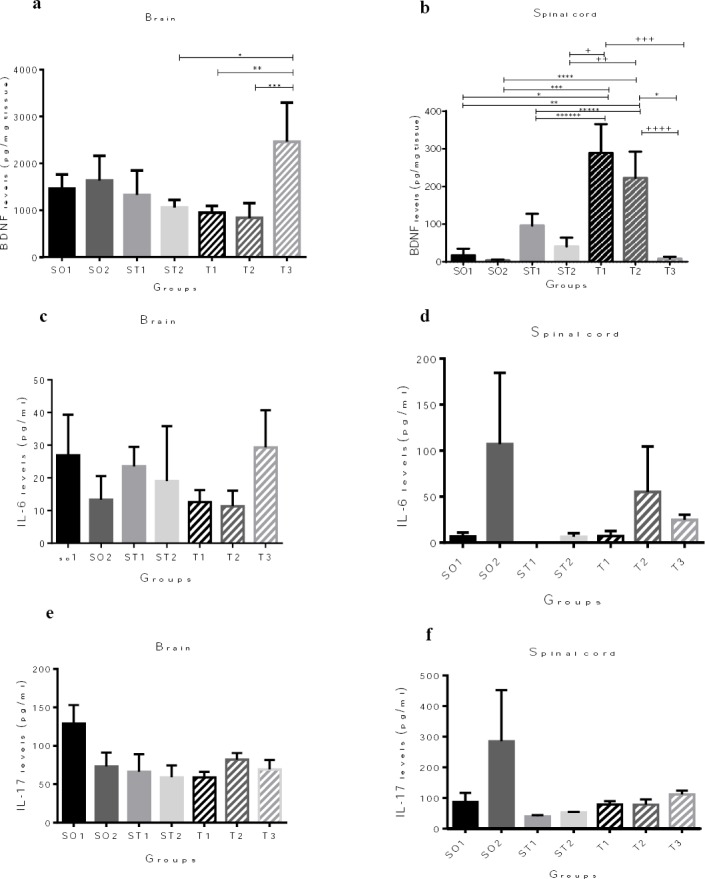
Protein quantification of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and interleukin-17A (IL-17A) expression in the whole brain and spinal cord by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). (a) Animals in T3 group showed significantly increased BDNF protein levels in the brain compared to ST2, T1, and T2 experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) mice (*P = 0.048; ** P = 0.041, *** P =0.023, respectively). (c), (d), (e), and (f) There are no differences between the experimental groups in terms of IL-6 and IL-17 protein levels in the brain and spinal cord. (b) Animals in SO1 and SO2 groups, also EAE animals in ST1, ST2, and T3 groups showed significantly decreased BDNF expression in the spinal cord compared to EAE mice in T1 and T2 groups (*P= 0.001, **P= 0.008, *** P = 0.000; **** P = 0.001, ***** P = 0.003; ****** P= 0.041, + P = 0.001; ++ P = 0.008, +++ P = 0.000, ++++ P =0.001). Results are shown as pg/mg tissue BDNF and pg/ml IL-6 and Il-17. Data are given as mean ± SEM analyzed by one way ANOVA and LSD’s post hoc test. SO1 (sham operated 1, sham+ PBS); SO2 (sham operated 2, sham+ PBS+ riboflavin); ST1 (sham treatment 1, EAE+ Veh1); ST2 (sham treatment 2, EAE +Veh2); T1 (treatment 1, EAE + INFβ-1a); T2 (treatment 2, EAE +Riboflavin); T3 (Treatment 3, EAE + INFβ-1a + Riboflavin); BDNF (brain-derived neurotrophic factor). The experiments were repeated three times in triplicates. (n = 8 for all groups)
