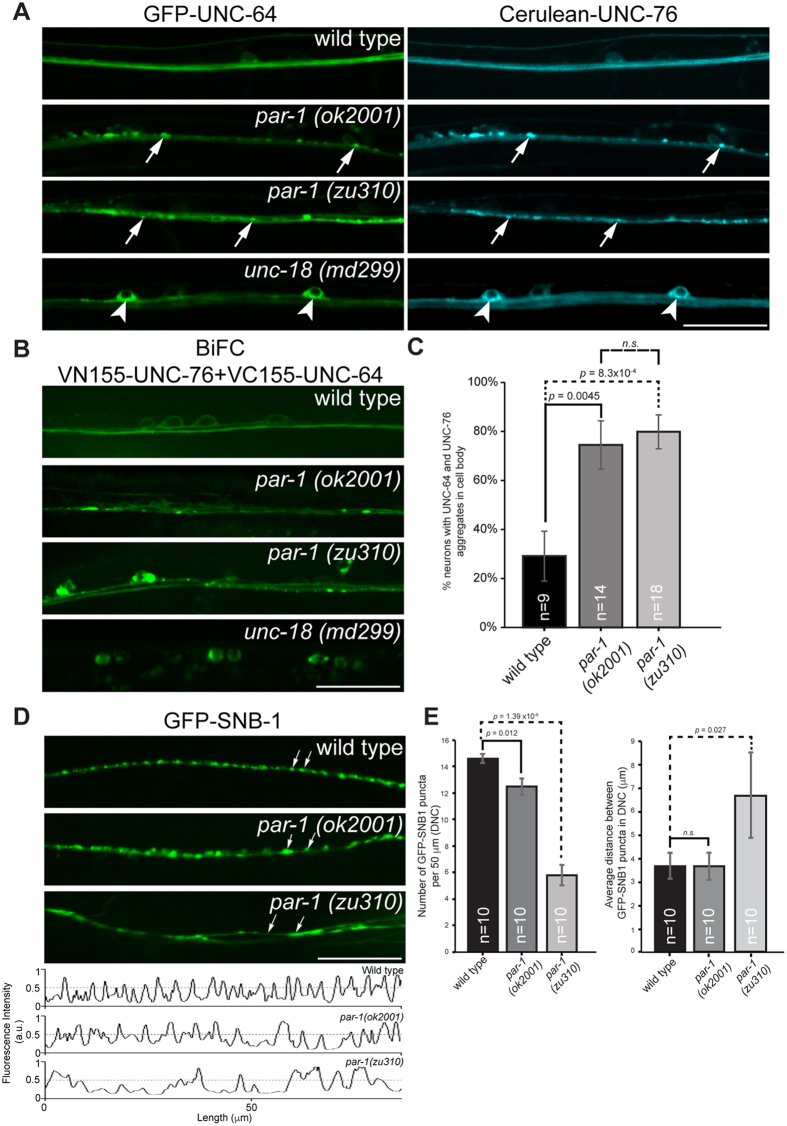
Figure 3. Axonal transport and synaptic defects in par-1 mutants.
(A) Localization of GFP-UNC-64 and Cerulean-UNC-76 in ventral nerve cords (VNC) of various C. elegans strains. GFP-UNC-64 and Cerulean-UNC-76 are uniformly distributed in VNC of wild type transgenic worms expressing either protein (top panel). Abnormal axonal aggregates (arrows) of both proteins appear in both par-1 mutants (middle 2 panels). In unc-18 mutants, strong cell body retention of both proteins (arrowheads) is observed, consistent with UNC-18’s function in ER export of UNC-64 (bottom panel). Scale bar, 20 μm. (B) Localization of bimolecular fluorescence complexes (BiFC) containing VN155-UNC-76 and VC155-UNC-64 in various C. elegans strains. BiFC complexes exhibit uniform distribution in wild type worms (top panel). Cell body retention of BiFC complexes similar to their singly expressed counterparts in unc-18 mutants supports that they are not artefacts arising from GFP complementation (bottom panel). par-1 mutants exhibit abnormal aggregation of the complexes in VNC axons and neuronal cell bodies distinct from those in unc-18 mutants. Scale bar, 20 μm. (C) Quantification of neurons exhibiting cell body aggregates of UNC-64 and UNC-76 as exemplified in (B) (p < 0.01, t-test). Error bars represent S.E.M. (D) Defective presynaptic organization in par-1 mutants. GFP-SNB-1 was used here as a marker for presynaptic specializations. Wild type worms display small regularly spaced GFP-SNB-1 punctae in dorsal nerve cords (DNC). In par-1 mutants, these punctae are replaced by large abnormal aggregates (arrows, par-1 (ok2001) panel) or become diffusely distributed (arrows, par-1 (zu310) panel). Anomalies are also observed in VNC (see Supplementary Fig. S3). Scale bar, 20 μm. (E) Quantification of presynaptic specializations in wild type and par-1 mutants. Line scans were drawn along the DNC using ImageJ software (Fig. 3D, bottom panel). Fluorescent intensity peaks greater than 0.5 were considered as genuine GFP-SNB-1 punctae and included for the analyses. GFP-SNB-1 punctae densities along a 50 μm stretch of the DNC and average inter-punctae distances were calculated. par-1 mutants exhibit significantly lower GFP-SNB-1 densities against wild type worms (p < 0.05, t-test). Furthermore, par-1 (zu310) exhibited larger inter-punctae distances indicative of presynaptic organization defects (p < 0.05, t-test). Error bars represent S.E.M.