Fig.3. Induction of DARPP-32 by RA is PKC-dependent.
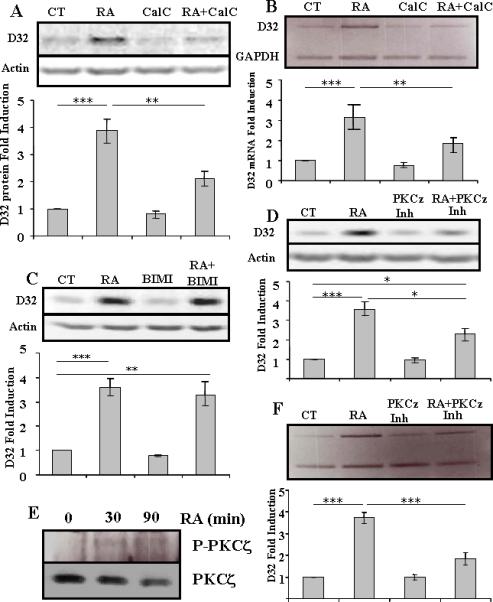
(A) Primary striatal neurons were treated with retinoic acid (RA) (10 μM), calphostin C (CalC) (250nM) or both for 24 hrs and DARPP-32 protein levels were measured. (**p<0.01 and ***p<0.001). (B) Primary striatal neurons were treated with retinoic acid (RA) (10 μM), calphostin C (CalC) (250nM) or both for 24 hrs and DARPP-32 mRNA levels were measured. (**p<0.01 and ***p<0.001). (C) Primary striatal neurons were treated with retinoic acid (RA) (10 μM), bisindolylmaleimide I (Bis) (100nM) or both for 24 hrs and DARPP-32 protein levels were measured (**p<0.01 and ***p<0.001). (D) Primary striatal neurons were treated with retinoic acid (RA), myristolated pseudosubstrate PKCζ Inhibitor (PKCζ Inh) or both for 24 hrs, and DARPP-32 protein levels were measured. (*p<0.05 and ***p<0.001). N =3 for all treatments, and statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post-hoc test. (E) Primary striatal neurons were treated with retinoic acid (RA) (10 μM) for 30 or 90 minutes and proteins were immunoprecipitated with anti-PKCζ and blotted for PKCζ and phospho-PKCζ. Phospho-PKCζ is detectable only after treatment with retinoic acid, but levels of total PKCζ are not increased. Representative of 3 experiments. (F) Primary striatal neurons were treated with retinoic acid (RA), myristolated pseudosubstrate PKCζ Inhibitor (PKCζ Inh) or both for 8 hrs, and DARPP-32 mRNA, relative to actin, levels were measured. Representative of three experiments. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA (p<0.0001) and significant differences were found between groups (***p<0.001)
