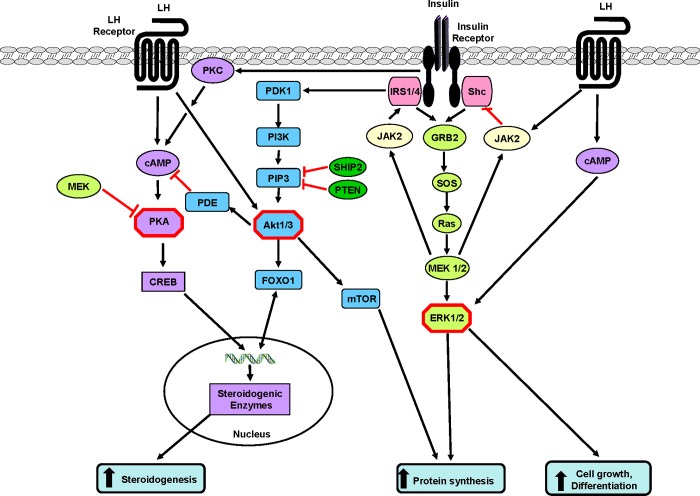
Figure 3. Some possible sites of cross-talk (critical nodes) between the insulin and LH signalling pathways in theca cells.
Insulin signalling through Akt1 can stimulate PDE to inhibit the degradation of cAMP and so enhance LH-stimulated androgen production; similarly, insulin acting via Akt1 and FOXO1 can enhance LH-stimulated steroidogenesis. Acting via mTOR and/or ERK, LH can enhance cell proliferation and protein synthesis and it can inhibit apoptosis. LH acting directly or via cAMP can enhance insulin stimulation of ERK, whereas, at the same time, LH can stimulate JAK2 which inhibits Shc activation of ERK. The balance of these opposing actions can modulate insulin-stimulated cell proliferation and protein synthesis. Stimulatory connections are shown in black and inhibitory ones are shown in red.