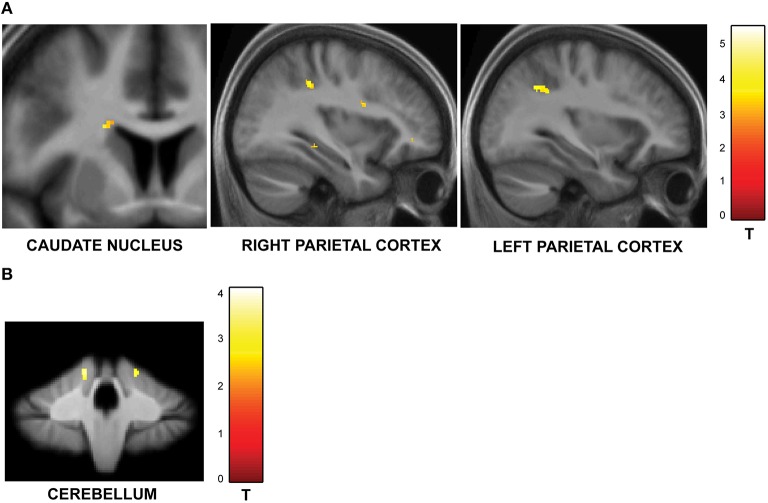
Figure 3.
Functional imaging results: effect of number of intervals. (A) Brain areas that encode temporal memory as a function of increasing number of intervals. The activity in the caudate and the inferior parietal cortex was found to increase parametrically with the number of intervals. The MNI coordinates of these areas are listed in Table 2A. (B) Brain areas that encode temporal memory as a function of decreasing number of intervals. BOLD responses in the cerebellum was found to vary as a function of decreasing number of intervals. The MNI coordinates are provided in Table 2B.