Fig. 4.
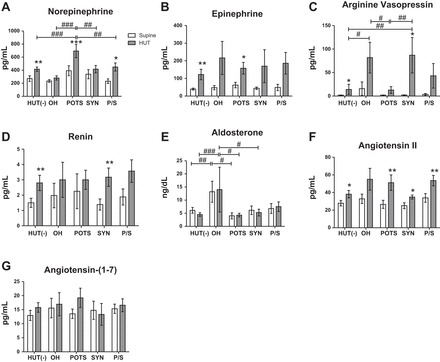
Orthostatic changes in NE (A), Epi (B), AVP (C), renin (D), Aldo (E), ANG II (F), and ANG-(1–7) (G) in children in five diagnostic HUT subgroups. There were no differences between groups at baseline for all neurohumoral measures except Aldo. HUT(−) subjects (n = 18) had a significant increase in NE, Epi, AVP, ANG II, and renin from the supine position to HUT. POTS subjects (n = 7) had significantly higher NE than all other groups during HUT and a significant increase in Epi upon HUT. OH (n = 5) and Syn (n = 8) groups had exaggerated increases in AVP upon standing and significantly higher AVP during HUT compared with HUT(−) and POTS groups. Increased renin was observed in all groups from the supine position to HUT. Aldo was significantly higher in the supine position and during HUT for OH subjects. ANG II increased upon standing in all groups, and P/S subjects (n = 10) had significantly higher ANG II than HUT(−) and Syn groups. There were no differences between or among groups for ANG-(1–7). Supine position vs. HUT: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001; HUT(−) vs. HUT(+) subjects: #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, and ###P < 0.001.
