Fig. 1.
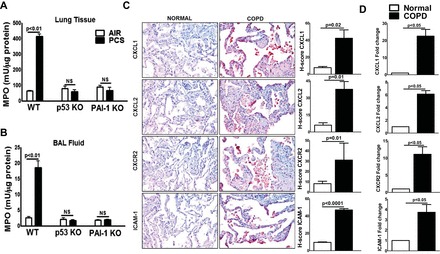
Induction of p53 and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) contributes to lung inflammation in mice exposed to passive cigarette smoke (CS) and patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Lung tissues (A) and bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluids (B) collected from wild-type (WT) and p53- and PAI-1-deficient (KO) mice (n = 5/group) exposed to ambient air (AIR) or passive CS (PCS) for 20 wk were analyzed for myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity. MPO activity quantification is expressed as mean ± SD of 3 independent analyses. C: lung sections from patients with COPD and histologically “normal” donor subjects (n = 5) were subjected to immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis using CXCL1, CXCL2, CXCR2, and ICAM-1 antibodies. Images are representative of IHC staining pattern of 10 fields (×200 magnification) and graphs show IHC scores (H-scores). D: total RNA isolated from the lung tissues of patients with COPD or normal subjects (n = 5) were analyzed for CXCL1, CXCL2, CXCR2, and ICAM-1 mRNAs by real-time PCR. Bar represents mean ± SD of 3 independent analyses. NS, not significant.
