Fig. 6.
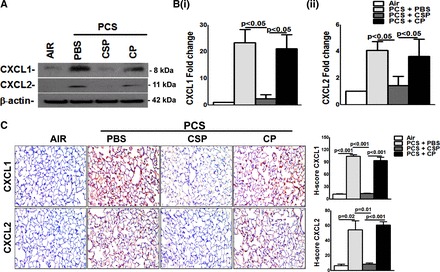
Inhibition of PCS exposure induced pulmonary CXCL1 and CXCL2 expression by CSP. WT mice were exposed to ambient air or PCS (n = 5/group) as described in materials and methods for 5 days/wk. After 4 wk of PCS exposure, mice exposed to PCS were intraperitoneally injected with or without 18.75 mg/kg body wt of CSP or CP once every week for 4 more wk. After 20 wk of PCS exposure, mice were euthanized. A: lung homogenates from these mice (n = 5/group) were immunoblotted for CXCL1 and CXCL2 expression. Representative blot from triplicate analyses is showed. B: total RNA from the lungs of these mice (n = 5/group) was tested for changes in the expression of CXCL1 (i) and CXCL2 (ii) and β-actin mRNA. Individual bars represent mean ± SD of triplicate analyses. C: lung sections from WT mice (n = 5/group) were subjected to IHC analysis by using anti-CXCL1 and CXCL2 antibody. Images are representative of IHC staining pattern of 10 fields (×200 magnification) and graph shows the H-scores.
