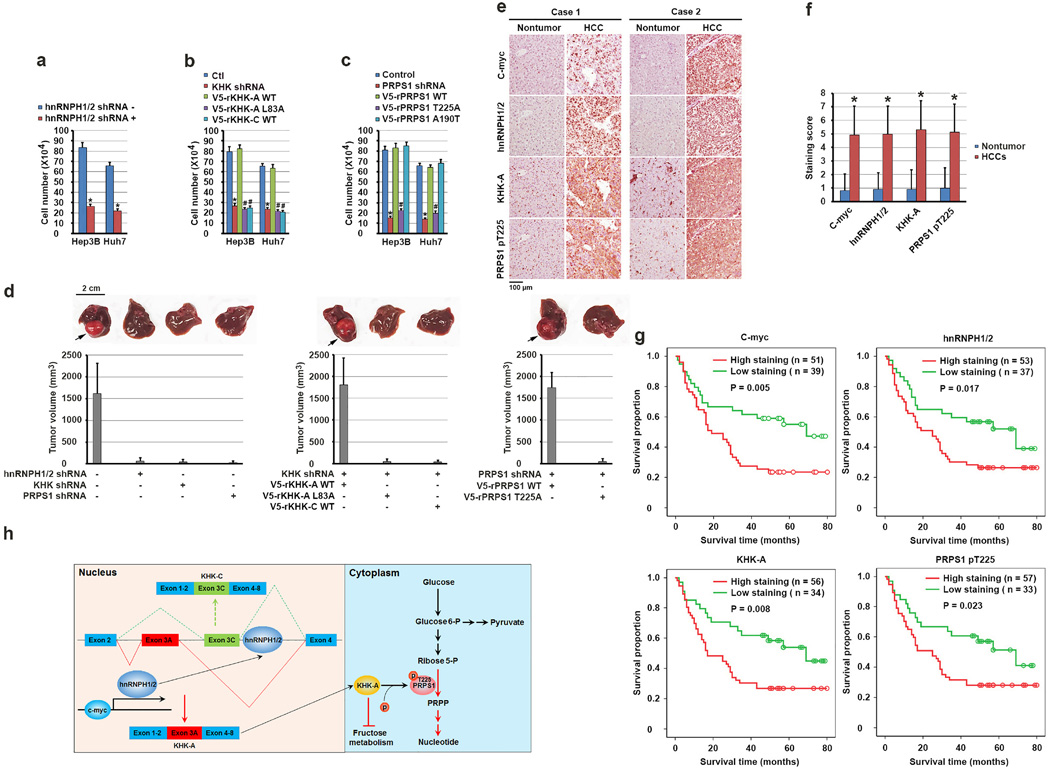
Figure 6. KHK-A–dependent phosphorylation of PRPS1 promotes hepatocellular tumorigenesis and is associated with the pathogenesis of HCC.
(a, b, c) A total of 1 × 105 Hep3B and Huh7 cells with or without expression of hnRNPH1/2 shRNA (a), KHK shRNA (b), PRPS1 shRNA (c) and with or without reconstituted expression of the indicated WT or mutated proteins were plated for 3 days. The cells were then collected and counted. The data represent the mean ± s.d. from n = 3 independent experiments. A two-tailed Student’s t test was used. * represents P < 0.01 between the cells with or without hnRNPH1/2 depletion (a), the cells with or without KHK depletion (b), the cells with or without PRPS1 depletion (c). # represents P < 0.01 between the KHK-depleted cells with reconstituted expression of WT rKHK-A and the KHK-depleted cells with reconstituted expression of rKHK-A L83A and WT rKHK-C (b), and between PRPS1-depleted cells with reconstituted expression of WT rPRPS1 and rPRPS1 T225A (c).
(d) A total of 1 × 106 Huh7 cells with or without expression of hnRNPH1/2 shRNA, KHK shRNA, or PRPS1 shRNA and with or without reconstituted expression of their WT counterparts and the indicated mutants were intrahepatically injected into athymic nude mice (n = 5 mice/group). The mice were sacrificed and examined for tumor growth 28 days after injection. The arrows point to the tumors.
(e) Immunohistochemical staining of 90 human HCC and matched non-tumor tissue samples for the indicated antibodies was performed. Representative photos of stains in two cases are shown.
(f) c-Myc, hnRNPH1/2, and KHK-A expression levels and PRPS1 T225 phosphorylation levels in HCC and matched non-tumor liver samples were obtained from n = 90 patients. The indicated staining scores in HCC and matched non-tumor liver samples were compared using a paired Student t-test. *p < 0.001.
(g) Kaplan-Meier plots of the overall survival rates in the patients (n = 90) with HCC in the groups with high (staining score, 5–8.0) and low (staining score, 0–4.0) expression of c-Myc, hnRNPH1/2, and KHK-A and phosphorylation of PRPS1 T225. The P values were calculated using the log-rank test.
(h) A mechanism of KHK-A–promoted de novo nucleotide synthesis. c-Myc enhances the expression of hnRNPH1 and hnRNPH2, which bind to the exon 3C-3'/intron region of KHK, leading to alternative splicing of KHK pre-mRNA for KHK-A expression and reduced fructose metabolism. KHK-A phosphorylates and activates PRPS1, resulting in enhanced production of nucleotide and nucleotide acid derived from glycolysis and promotion of hepatocellular tumorigenesis.