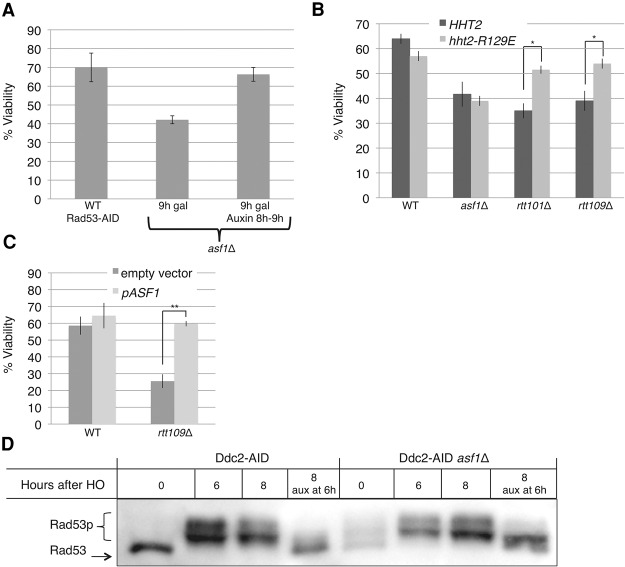
Figure 6.
Rescue of the recovery defect in asf1Δ, rtt109Δ, and rtt101Δ. (A) Reducing Rad53 levels for 1 h rescues the recovery defect in two-DSB asf1Δ. Two-DSB asf1Δ cells containing Rad53-AID (YMT222) were allowed to repair the DSB for 8 h prior to treatment with 500 µM auxin. One hour after treatment with auxin, asf1Δ cells were plated on galactose plates. Colony numbers were normalized to 0 h of YEPD. The viability of wild-type cells with Rad53-AID is shown as a reference. n = 3. Error bars indicate standard errors. (B) Histone H3-R129E rescues the recovery defect of rtt101Δ and rtt109Δ but not asf1Δ. n = 3. Error bars indicate standard errors. (*) P < 0.05. (C) Overexpression of Asf1 rescues rtt109Δ. Wild type (YFA01) and rtt109Δ (YFA06) were transformed with either an empty vector or pASF1. n ≥ 3. (**) P < 0.005. (D) Asf1 is required for complete dephosphorylation of Rad53 after Ddc2 degradation. A strain containing a single irreparable DSB with Ddc2-AID and either wild-type (left four lanes) or asf1Δ (right four lanes). Six hours after HO induction, the culture was split and half was treated with 500 µM auxin for 2 h (8 h after HO induction).