Figure 7. Increased cardiac fatty acid oxidation, ROS formation and cardiolipin remodeling.
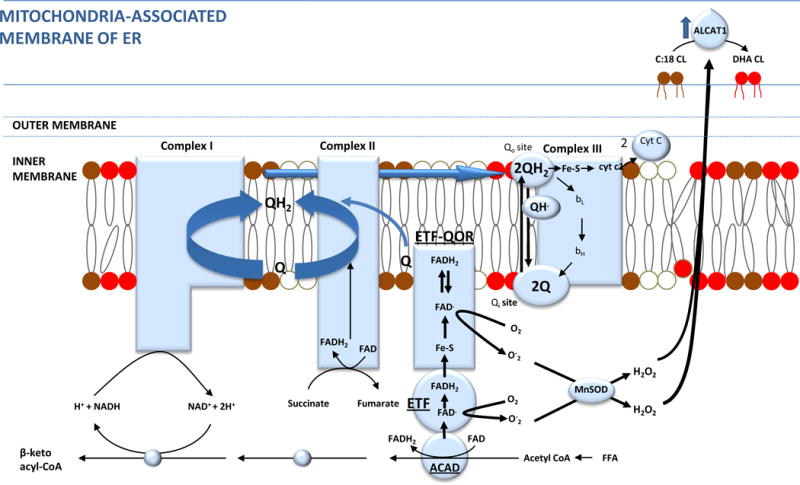
Insulin resistance-induced increased cardiac β oxidation of free fatty acids (FFA) causes greater H2O2 production than increased glucose oxidation because of increased electron leakage from the electron transfer flavoprotein (ETF) complex. These ROS activate Acyl-CoA:lysocardiolipin acyltransferase 1 (ALCAT1). ALCAT1, located in the mitochondrial associated membrane (MAM) of the ER, which causes pathologic remodeling of cardiolipin from tetra 18:2 cardiolipin to cardiolipin with highly unsaturated fatty acid side chains and cardiolipin deficiency due to oxidative damage. This reduces ETC electron flux, ATP synthesis, and further increases ROS.
