Figure 8. Diabetes-induces increased mitochondrial fission.
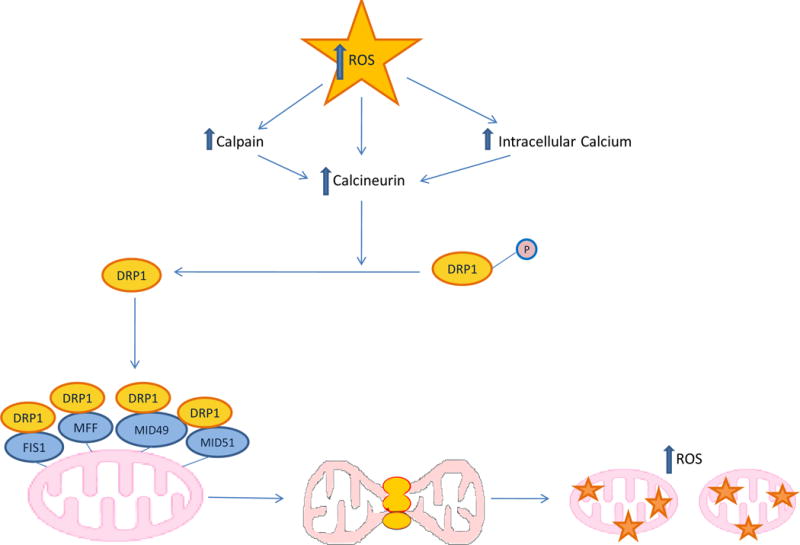
Increased ROS from either excess glucose in vascular cells or fatty acids in cardiomyocytes increases intracellular Ca++. Increased Ca++ activates the calcium-activated neutral cysteine protease calpain, which activates the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent/CaM) (Ca2+)serine/threonine phosphatase calcineurin. Calcineurin dephosphorylates the GTPase dynamin-related protein 1 (DRP1), which is then recruited from the cytosol to the mitochondrial outer membrane where it binds to four DRP1 receptors- — mitochondrial fission factor (MFF), Mitochondrial dynamics protein of 49 kDa (MID49) and 51 kDa (MID51), and FIS1. Drp1 oligimerization provides the mechanical force to constrict mitochondrial membranes and fragment the organelle (mitochondrial fission). Increased fission causes further increases in ROS production and mitochondrial dysfunction. FIS1, Mitochondrial fission 1 protein.
