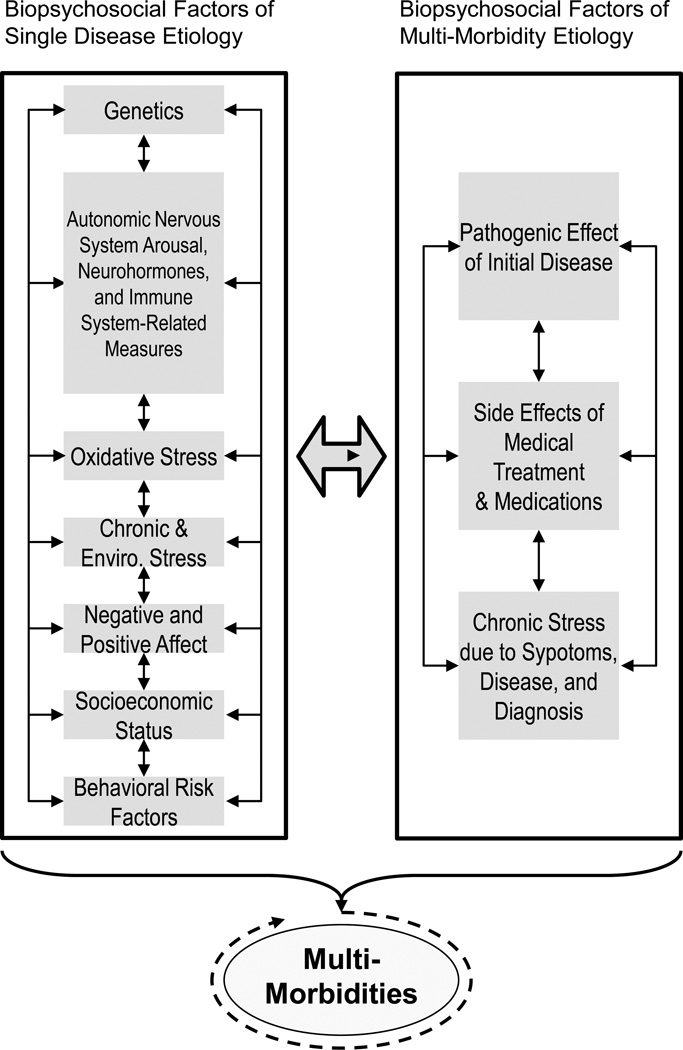
Figure 2.
Reciprocal Effects of Biopsychosocial Factors of Single Disease and Multi-Morbidity Etiology
(left panel) includes the same factors, such as shared genes, autonomic arousal, neurohormones, immune system-related activity, negative and positive affective dispositions, shared behavioral risk factors, etc., as in Figure 1. In one scenario, two or more diseases emerge more or less simultaneously because of a shared subset of the factors, listed in the left panel. The right panel depicts the staggered emergence of other conditions as a function of downstream biological effects of the initial disease, acute/chronic stress induced by diagnosis and treatment of the initial disease and/or the side-effects of medical treatment.