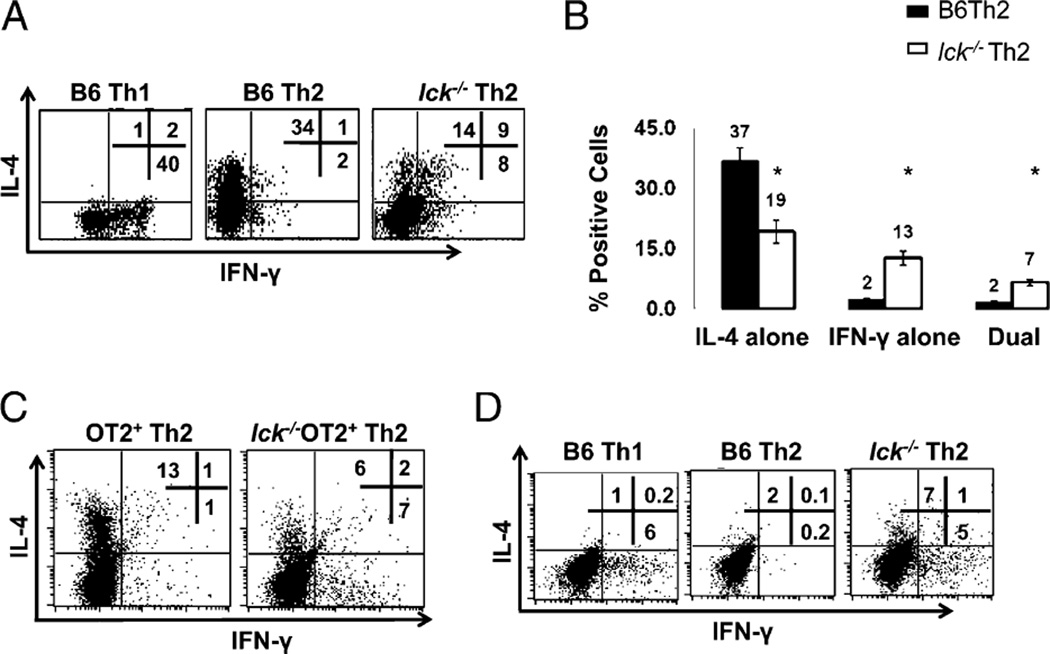
FIGURE 1.
Lck-deficient Th2 skewed cells produce IFN-γ and have reduced IL-4. A, lck−/− Th2 skewed cells have abnormal IL-4 and IFN-γ expression. CD4+ splenocytes were stimulated under Th1 and Th2 conditions for 7 d and analyzed for IL-4 and IFN-γ by ICCS. B, Percentage of cells producing IL-4 and IFN-γ in B6 and lck−/− Th2 cells skewed for 7 d. The graph illustrates the average of >20 ICCS experiments performed on CD4+ cells. The asterisk indicates that the data are statistically significant (Student unpaired t test; p < 0.05). C, Ag-specific skewing. CD4+ splenocytes from OTII and lck−/− OTII mice were skewed in the presence of APCs and OVA peptide. The cells were then restimulated with APCs and OVA peptide for 5 h and analyzed for IL-4 and IFN-γ as in A. The data are representative of three experiments. D, IFN-γ protein expression is elevated in day 3 lck−/− Th2 cultures. Bulk CD4+ cells were skewed under Th1 and Th2 conditions and then analyzed for IL-4 and IFN-γ by ICCS. The cells were initially gated on CD4 expression. The results are representative of three experiments.