Figure 8.
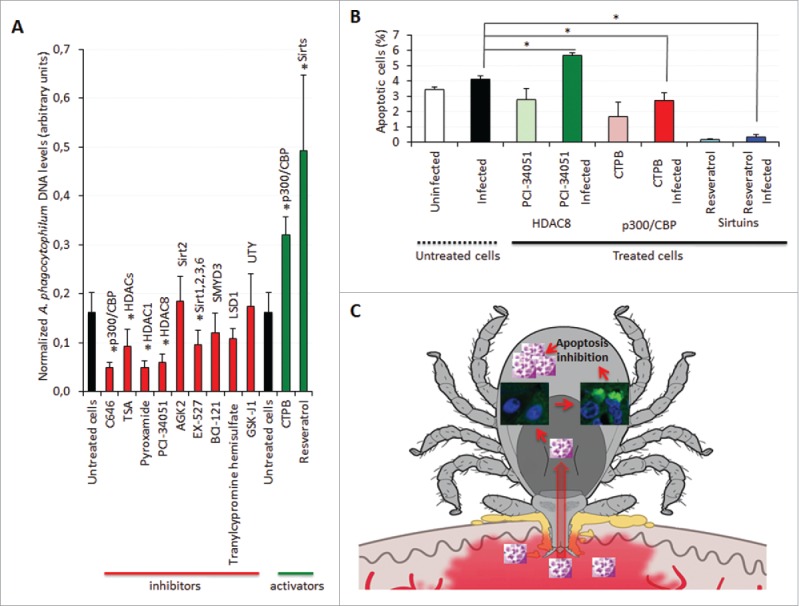
Characterization of the function of I. scapularis HMEs during A. phagocytophilum infection. (A) A. phagocytophilum DNA levels were determined in infected ISE6 tick cells untreated or treated for 72 h with C646 to inhibit p300/CBP, Trichostatin A (TSA) to inhibit HDACs, Pyroxamide to inhibit HDAC1, PCI-34051 to inhibit HDAC8, AGK2 to inhibit Sirt2, EX-527 to inhibit Sirt1/Sirt2/Sirt3/Sirt6, BCI-121 to inhibit SMYD3, Tranylcypromine hemisulfate to inhibit LSD1, GSK-J1 to inhibit UTY, CTPB to activate p300/CBP and Resveratrol to activate Sirtuins. Bacterial DNA levels were determined by msp4 real-time PCR normalizing against tick 16S rDNA. Results are shown as Ave+SD normalized Ct values and were compared between untreated and treated cells by Student's t-test with unequal variance (*P < 0.05; N = 4). (B) The percentage of apoptotic cells was determined by flow cytometry in uninfected and infected ISE6 tick cells untreated or treated for 72 h with PCI-34051 to inhibit HDAC8, CTPB to activate p300/CBP and Resveratrol to activate Sirtuins. Results are represented as Ave+SD and compared between untreated and treated infected cells by Student's t-test with unequal variance (*P <0.05; N = 4). (C) Schematic representation of the role of tick Sirtuins during A. phagocytophilum infection. A. phagocytophilum manipulates tick cell epigenetics to increase IsSirtuin levels resulting in the inhibition of cell apoptosis to facilitate pathogen infection and multiplication.
