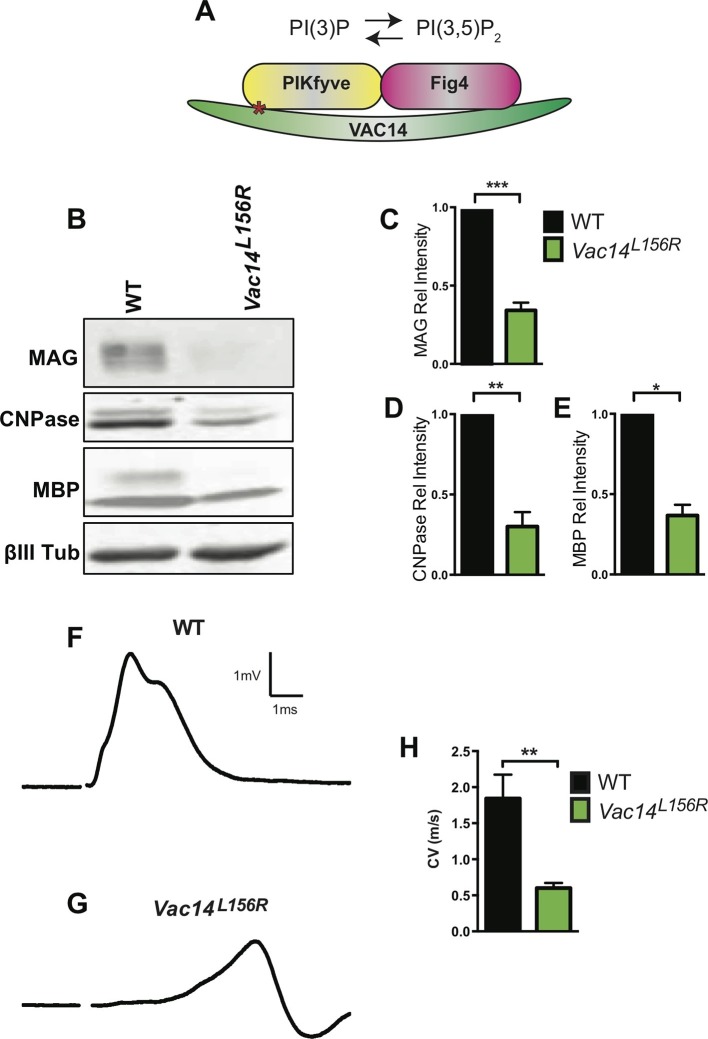
Figure 7. Homozygosity for VAC14L156R leads to CNS hypomyelination and impaired conduction of compound action potentials.
(A) Schematic of the PIKfyve/Vac14/Fig4 enzyme complex and its phosphoinositide products PI(3)P and PI(3,5)P2. The red asterisk in VAC14 indicates the L156R point mutation that perturbs the interaction with PIKfyve, but not with Fig4. (B) Western blot analysis of brain membranes prepared from adult (P90-120) WT and VAC14L156R/VAC14L156R littermate mice revealed a reduction in the myelin markers MAG, CNPase, and MBP. Anti-class III β-tubulin (βIII-Tub), a neuronal marker, is shown as a loading control. (C-E) Quantification of protein bands detected by Western blotting, shows a significant decrease in MAG, CNPase, and MBP in VAC14 mutant brain tissue (n = 3 independent blots per genotype). Unpaired Student’s t-test; mean value ± SEM. ***p<0.001, **p=0.0015 and *p=0.0238. (F and G) Representative CAP traces recorded from acutely isolated optic nerves of WT and VAC14L156T homozygous mice. (H) Quantification of average conduction velocity (CV) of largest amplitude peaks identified in F and G. Results are shown as mean value ± SEM, unpaired Student’s t-test, **p=0.0063. WT n = 6 nerves, 3 mice and for Vac14L156R mutants n = 6 nerves, 3 mice. Toluidine blue staining of epoxy resin embedded optic nerve sections from VAC14L156R/VAC14L156R mice is shown in Figure 7—figure supplement 1.
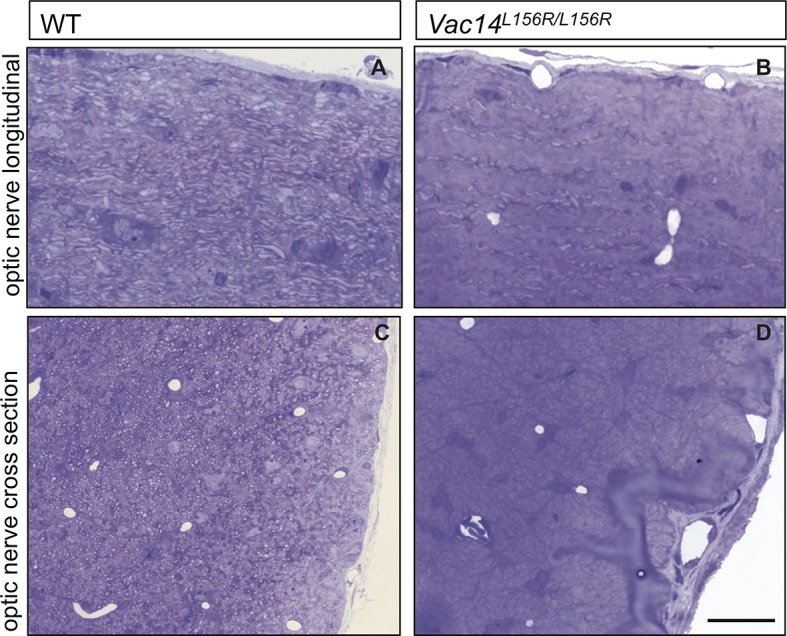
Figure 7—figure supplement 1. Severe optic nerve hypomyelination in VAC14L156R/L156R mice.